基于Android 6.0源码, 从Window角度来分析Activity启动过程。
一. 概述
前面的文章startActivity启动过程分析,已从AMS的角度讲述了Activity启动过程,那么本文从WMS的角度说一说这个过程。
先用上一篇文章的流程图来简单回顾一下:点击查看大图
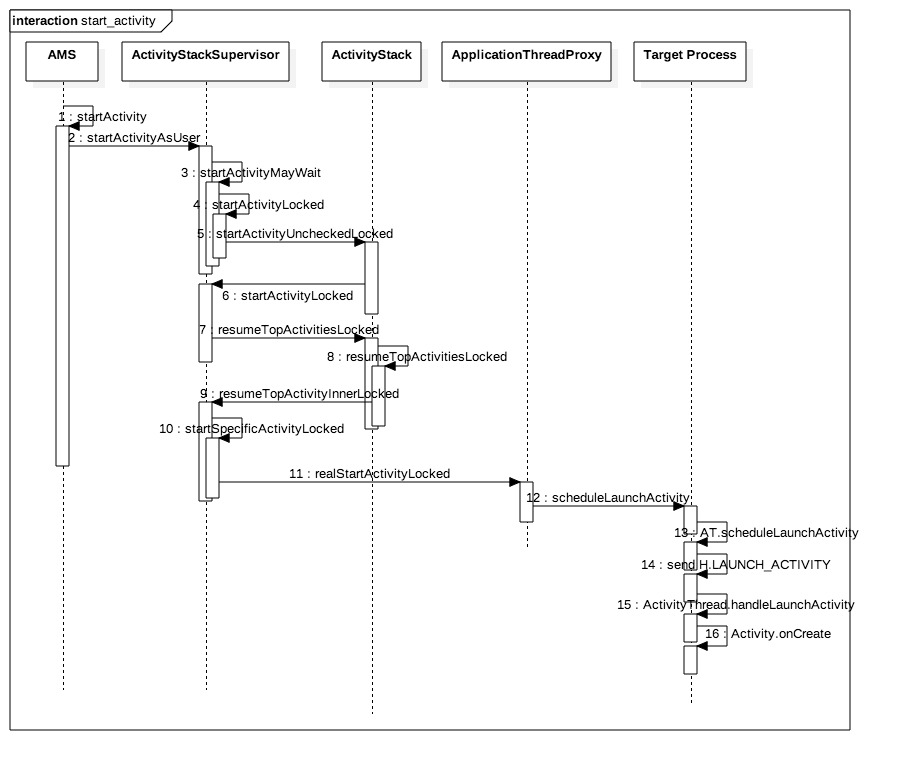
接下来,从文章startActivity启动过程分析的小节[2.10] AS.startActivityLocked()开始说起。
二. Window处理流程
2.1 AS.startActivityLocked
[-> ActivityStack.java]
final void startActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, boolean newTask,
boolean doResume, boolean keepCurTransition, Bundle options) {
TaskRecord rTask = r.task;
final int taskId = rTask.taskId;
if (!r.mLaunchTaskBehind && (taskForIdLocked(taskId) == null || newTask)) {
insertTaskAtTop(rTask, r);
//将Window相应task移至顶部[见小节2.1.1]
mWindowManager.moveTaskToTop(taskId);
}
TaskRecord task = null;
if (!newTask) {
boolean startIt = true;
for (int taskNdx = mTaskHistory.size() - 1; taskNdx >= 0; --taskNdx) {
task = mTaskHistory.get(taskNdx);
if (task == r.task) {
if (!startIt) {
task.addActivityToTop(r);
r.putInHistory();
//创建AppWindowToken对象 [见小节2.1.2]
mWindowManager.addAppToken(task.mActivities.indexOf(r), r.appToken,
r.task.taskId, mStackId, r.info.screenOrientation, r.fullscreen,
(r.info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_SHOW_FOR_ALL_USERS) != 0,
r.userId, r.info.configChanges, task.voiceSession != null,
r.mLaunchTaskBehind);
return;
}
break;
}
...
}
}
...
if (!isHomeStack() || numActivities() > 0) {
//当切换到新的task,或者下一个activity进程目前并没有运行
boolean showStartingIcon = newTask;
ProcessRecord proc = r.app;
if (proc == null) {
proc = mService.mProcessNames.get(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo.uid);
}
if (proc == null || proc.thread == null) {
showStartingIcon = true;
}
if ((r.intent.getFlags() & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_ANIMATION) != 0) {
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(AppTransition.TRANSIT_NONE, keepCurTransition);
mNoAnimActivities.add(r);
} else {
//设置transition方式[见小节2.1.3]
mWindowManager.prepareAppTransition(newTask
? r.mLaunchTaskBehind
? AppTransition.TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN_BEHIND
: AppTransition.TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN
: AppTransition.TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_OPEN, keepCurTransition);
mNoAnimActivities.remove(r);
}
mWindowManager.addAppToken(...);
boolean doShow = true;
if (newTask) {
if ((r.intent.getFlags() & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_RESET_TASK_IF_NEEDED) != 0) {
resetTaskIfNeededLocked(r, r);
doShow = topRunningNonDelayedActivityLocked(null) == r;
}
} else if (options != null && new ActivityOptions(options).getAnimationType()
== ActivityOptions.ANIM_SCENE_TRANSITION) {
doShow = false;
}
if (r.mLaunchTaskBehind) {
mWindowManager.setAppVisibility(r.appToken, true);
ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null, 0);
} else if (SHOW_APP_STARTING_PREVIEW && doShow) {
ActivityRecord prev = mResumedActivity;
mWindowManager.setAppStartingWindow(
r.appToken, r.packageName, r.theme,
mService.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(
r.info.applicationInfo), r.nonLocalizedLabel,
r.labelRes, r.icon, r.logo, r.windowFlags,
prev != null ? prev.appToken : null, showStartingIcon);
r.mStartingWindowShown = true;
}
} else {
mWindowManager.addAppToken(...);
...
}
if (doResume) {
//该方法内部调用AS.resumeTopActivityInnerLocked [见流程2.2]
mStackSupervisor.resumeTopActivitiesLocked(this, r, options);
}
}
此处涉及WMS的有以下过程:
- WMS.moveTaskToTop:将Window相应task移至顶部;
- WMS.addAppToken:创建AppWindowToken对象atoken,并添加到mTokenMap;
- WMS.prepareAppTransition:设置transition方式以及5s超时消息;
- WMS.setAppStartingWindow:创建startingData启动数据,并发送消息到”android.display”线程来处理ADD_STARTING消息。
2.1.1 WMS.moveTaskToTop
public void moveTaskToTop(int taskId) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
synchronized(mWindowMap) {
Task task = mTaskIdToTask.get(taskId);
if (task == null) {
return;
}
final TaskStack stack = task.mStack;
final DisplayContent displayContent = task.getDisplayContent();
//将该task所属的栈 移至display的顶部
displayContent.moveStack(stack, true);
if (displayContent.isDefaultDisplay) {
final TaskStack homeStack = displayContent.getHomeStack();
if (homeStack != stack) {
//当非home栈移至顶部,则把home栈移至底部
displayContent.moveStack(homeStack, false);
}
}
//将该task 移至栈的顶部
stack.moveTaskToTop(task);
if (mAppTransition.isTransitionSet()) {
task.setSendingToBottom(false);
}
//更新窗口布局
moveStackWindowsLocked(displayContent);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
2.1.2 WMS.addAppToken
public void addAppToken(int addPos, IApplicationToken token, int taskId, int stackId,
int requestedOrientation, boolean fullscreen, boolean showForAllUsers, int userId,
int configChanges, boolean voiceInteraction, boolean launchTaskBehind) {
long inputDispatchingTimeoutNanos;
inputDispatchingTimeoutNanos = token.getKeyDispatchingTimeout() * 1000000L;
synchronized(mWindowMap) {
AppWindowToken atoken = findAppWindowToken(token.asBinder());
...
//创建AppWindowToken对象
atoken = new AppWindowToken(this, token, voiceInteraction);
atoken.inputDispatchingTimeoutNanos = inputDispatchingTimeoutNanos;
atoken.appFullscreen = fullscreen;
atoken.showForAllUsers = showForAllUsers;
atoken.requestedOrientation = requestedOrientation;
atoken.layoutConfigChanges = (configChanges &
(ActivityInfo.CONFIG_SCREEN_SIZE | ActivityInfo.CONFIG_ORIENTATION)) != 0;
atoken.mLaunchTaskBehind = launchTaskBehind;
//获取或创建相应的Task
Task task = mTaskIdToTask.get(taskId);
if (task == null) {
task = createTaskLocked(taskId, stackId, userId, atoken);
}
task.addAppToken(addPos, atoken);
//将该Token添加到mTokenMap
mTokenMap.put(token.asBinder(), atoken);
atoken.hidden = true;
atoken.hiddenRequested = true;
}
}
该方法的主要功能:创建AppWindowToken对象atoken,并添加到mTokenMap。另外,input超时时长为5s.
2.1.3 WMS.prepareAppTransition
public void prepareAppTransition(int transit, boolean alwaysKeepCurrent) {
synchronized(mWindowMap) {
if (!mAppTransition.isTransitionSet() || mAppTransition.isTransitionNone()) {
mAppTransition.setAppTransition(transit);
} else if (!alwaysKeepCurrent) {
if (transit == AppTransition.TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN
&& mAppTransition.isTransitionEqual(
AppTransition.TRANSIT_TASK_CLOSE)) {
//正在打开新的task,取代关闭动画
mAppTransition.setAppTransition(transit);
} else if (transit == AppTransition.TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_OPEN
&& mAppTransition.isTransitionEqual(
AppTransition.TRANSIT_ACTIVITY_CLOSE)) {
//正在打开新的activity,取代关闭动画
mAppTransition.setAppTransition(transit);
}
}
if (okToDisplay() && mAppTransition.prepare()) {
mSkipAppTransitionAnimation = false;
}
if (mAppTransition.isTransitionSet()) {
mH.removeMessages(H.APP_TRANSITION_TIMEOUT);
mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.APP_TRANSITION_TIMEOUT, 5000);
}
}
}
2.1.4 WMS.setAppStartingWindow
public void setAppStartingWindow(IBinder token, String pkg,
int theme, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
CharSequence nonLocalizedLabel, int labelRes, int icon, int logo,
int windowFlags, IBinder transferFrom, boolean createIfNeeded) {
...
wtoken.startingData = new StartingData(pkg, theme, compatInfo, nonLocalizedLabel,
labelRes, icon, logo, windowFlags);
Message m = mH.obtainMessage(H.ADD_STARTING, wtoken);
mH.sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue(m);
}
该方法的主要功能是创建startingData启动数据,并发送消息到”android.display”线程来处理ADD_STARTING消息
2.2 AS.resumeTopActivityInnerLocked
private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, Bundle options) {
final ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(null);
...
//暂停上一个Activity
boolean dontWaitForPause = (next.info.flags&ActivityInfo.FLAG_RESUME_WHILE_PAUSING) != 0;
boolean pausing = mStackSupervisor.pauseBackStacks(userLeaving, true, dontWaitForPause);
//进程已存在的情况
if (next.app != null && next.app.thread != null) {
//activity正在成为可见[见小节2.2.1]
mWindowManager.setAppVisibility(next.appToken, true);
...
ArrayList<ResultInfo> a = next.results;
if (a != null) {
final int N = a.size();
if (!next.finishing && N > 0) {
next.app.thread.scheduleSendResult(next.appToken, a);
}
}
if (next.newIntents != null) {
next.app.thread.scheduleNewIntent(next.newIntents, next.appToken);
}
next.sleeping = false;
mService.showAskCompatModeDialogLocked(next);
next.app.pendingUiClean = true;
next.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(mService.mTopProcessState);
next.clearOptionsLocked();
//触发onResume
next.app.thread.scheduleResumeActivity(next.appToken, next.app.repProcState,
mService.isNextTransitionForward(), resumeAnimOptions);
mStackSupervisor.checkReadyForSleepLocked();
}else {
...
//目标Activity所属的进程不存在的情况
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true);
}
}
resumeTopActivityInnerLocke的过程分两种情况:
- 当目标Activity所属的进程已创建,则下一步调用到AT.scheduleResumeActivity;
- 当目标Activity所属的进程未创建,则先创建进程后,再调用AT.scheduleLaunchActivity;
2.2.1 WMS.setAppVisibility
public void setAppVisibility(IBinder token, boolean visible) {
AppWindowToken wtoken;
synchronized(mWindowMap) {
//从mTokenMap找到相应的Token对象
wtoken = findAppWindowToken(token);
mOpeningApps.remove(wtoken);
mClosingApps.remove(wtoken);
wtoken.waitingToShow = false;
wtoken.hiddenRequested = !visible;
if (okToDisplay() && mAppTransition.isTransitionSet()) {
//设置用于占位的动画
if (!wtoken.mAppAnimator.usingTransferredAnimation &&
(!wtoken.startingDisplayed || mSkipAppTransitionAnimation)) {
wtoken.mAppAnimator.setDummyAnimation();
}
wtoken.inPendingTransaction = true;
if (visible) {
mOpeningApps.add(wtoken);
wtoken.startingMoved = false;
wtoken.mEnteringAnimation = true;
if (wtoken.hidden) {
wtoken.allDrawn = false;
wtoken.deferClearAllDrawn = false;
wtoken.waitingToShow = true;
if (wtoken.clientHidden) {
wtoken.clientHidden = false;
wtoken.sendAppVisibilityToClients();
}
}
} else {
mClosingApps.add(wtoken);
wtoken.mEnteringAnimation = false;
}
if (mAppTransition.getAppTransition() == AppTransition.TRANSIT_TASK_OPEN_BEHIND) {
//后台启动的,则将启动中的Activity添加到mOpeningApps.
final WindowState win = findFocusedWindowLocked(getDefaultDisplayContentLocked());
if (win != null) {
final AppWindowToken focusedToken = win.mAppToken;
if (focusedToken != null) {
//强制加载动画
focusedToken.hidden = true;
mOpeningApps.add(focusedToken);
}
}
}
return;
}
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
wtoken.inPendingTransaction = false;
//设置AppWindowToken相应窗口可见
setTokenVisibilityLocked(wtoken, null, visible, AppTransition.TRANSIT_UNSET,
true, wtoken.voiceInteraction);
wtoken.updateReportedVisibilityLocked();
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
2.3 AT.handleLaunchActivity
scheduleLaunchActivity之后便调用到了handleLaunchActivity方法
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
handleConfigurationChanged(null, null);
//初始化WMS【见小节2.3.1】
WindowManagerGlobal.initialize();
//【见小节2.4】
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
if (a != null) {
r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
//【见小节2.5】
handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward,
!r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed);
...
}
...
}
2.3.1 WMS.initialize
public static void initialize() {
getWindowManagerService();
}
public static IWindowManager getWindowManagerService() {
synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {
if (sWindowManagerService == null) {
//获取AMS的binder代理
sWindowManagerService = IWindowManager.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService("window"));
sWindowManagerService = getWindowManagerService();
ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(sWindowManagerService.getCurrentAnimatorScale());
}
return sWindowManagerService;
}
}
该方法的功能是获取AMS的代理对象。
2.4 AT.performLaunchActivity
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
if (r.packageInfo == null) {
//创建LoadedApk对象
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
component = r.intent.resolveActivity(
mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component);
}
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
//创建ComponentName对象
component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
Activity activity = null;
//获取ClassLoader
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
//创建目标Activity对象
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
//创建Application对象
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
if (activity != null) {
Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity);
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
//变量赋值操作【见小节2.4.1】
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor);
...
//【见小节2.4.2】
if (r.isPersistable()) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
}
...
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
if (r.isPersistable()) {
if (r.state != null || r.persistentState != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state,
r.persistentState);
}
} else if (r.state != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state);
}
}
...
}
r.paused = true;
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
return activity;
}
该方法主要功能:
- 创建LoadedApk对象;
- 创建ComponentName对象;
- 获取ClassLoader;
- 创建目标Activity对象;
- 创建Application对象;
- 回调onCreate(),一般地该方法内执行setContentView()操作;
2.4.1 Activity.attach
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachHost(null /*parent*/);
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this); //创建PhoneWindow
mWindow.setCallback(this);
mWindow.setOnWindowDismissedCallback(this);
mWindow.getLayoutInflater().setPrivateFactory(this);
...
mUiThread = Thread.currentThread(); //获取UI线程
mMainThread = aThread;
mInstrumentation = instr;
mToken = token; //远程ActivityRecord的appToken的代理端
mIdent = ident;
mApplication = application; //所属的Appplication
mIntent = intent;
mReferrer = referrer;
mComponent = intent.getComponent();
mActivityInfo = info;
mParent = parent;
...
//设置并获取WindowManagerImpl对象
mWindow.setWindowManager(
(WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE),
mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(),
(info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0);
if (mParent != null) {
mWindow.setContainer(mParent.getWindow());
}
mWindowManager = mWindow.getWindowManager();
mCurrentConfig = config;
}
该方法主要功能是完成以下成员变量的赋值:
- mWindow:数据类型为PhoneWindow,继承于Window对象;
- mWindowManager:数据类型为WindowManagerImpl,实现WindowManager接口;
- mMainThread:当前线程的ActivityThread对象;
- mApplication:当前Activity所属的Application;
- mHandler:当前主线程的handler;
- mUiThread: 当前activity所在的主线程;
- mToken:远程ActivityRecord的appToken的代理端
- mDecor: Activity执行完resume之后创建的View对象;
WindowManagerImpl.mParentWindowWindow指向Window对象, Window.mWindowManager指向WindowManagerImpl对象,这两个对象相互保存对方的信息。
2.5 AT.handleResumeActivity
final void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean clearHide, boolean isForward, boolean reallyResume) {
//执行到onResume方法()[见小节2.5.1]
ActivityClientRecord r = performResumeActivity(token, clearHide);
if (r != null) {
final Activity a = r.activity;
boolean willBeVisible = !a.mStartedActivity;
...
if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
if (a.mVisibleFromClient) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
wm.addView(decor, l);
}
}
...
if (!r.activity.mFinished && willBeVisible
&& r.activity.mDecor != null && !r.hideForNow) {
...
mNumVisibleActivities++;
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
//添加视图[见小节2.5.2]
r.activity.makeVisible();
}
}
//resume完成
if (reallyResume) {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().activityResumed(token);
}
} else {
...
}
}
该过程的执行顺序:
- performResumeActivity:最终会调用到onResume()方法;
- makeVisible:一直调用到WMS,来进行添加视图;
2.5.1 AT.performResumeActivity
public final ActivityClientRecord performResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean clearHide) {
ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);
if (r != null && !r.activity.mFinished) {
if (clearHide) {
r.hideForNow = false;
r.activity.mStartedActivity = false;
}
r.activity.onStateNotSaved();
r.activity.mFragments.noteStateNotSaved();
if (r.pendingIntents != null) {
deliverNewIntents(r, r.pendingIntents);
r.pendingIntents = null;
}
if (r.pendingResults != null) {
deliverResults(r, r.pendingResults);
r.pendingResults = null;
}
//回调onResume
r.activity.performResume();
...
}
return r;
}
2.5.2 Activity.makeVisible
void makeVisible() {
if (!mWindowAdded) {
ViewManager wm = getWindowManager();
//【见小节2.6】
wm.addView(mDecor, getWindow().getAttributes());
mWindowAdded = true;
}
mDecor.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
此处getWindowManager获取的是WindowManagerImpl对象。
2.6 WMI.addView
[-> WindowManagerImpl.java]
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
//【见小节2.7】
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mDisplay, mParentWindow);
}
2.7 WMG.addView
[-> WindowManagerGlobal.java]
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
...
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;
//创建ViewRootImpl[见小节2.8]
ViewRootImpl root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
//[见小节2.9]
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
...
}
2.8 ViewRootImpl
[-> ViewRootImpl.java]
public ViewRootImpl(Context context, Display display) {
mContext = context;
//获取IWindowSession的代理类【见小节2.8.1】
mWindowSession = WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession();
mDisplay = display;
mThread = Thread.currentThread(); //主线程
mWindow = new W(this); //【见小节2.8.3】
mChoreographer = Choreographer.getInstance();
...
}
初始化成员变量:
- mWindowSession:WMS端的Session的代理对象;
- mWindow: 继承于IWindow.Stub的W对象;
- mChoreographer:绘制相关的对象;
2.8.1 WMG.getWindowSession
[-> WindowManagerGlobal.java]
public static IWindowSession getWindowSession() {
synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {
if (sWindowSession == null) {
try {
//获取IMS的代理类
InputMethodManager imm = InputMethodManager.getInstance();
//获取WMS的代理类
IWindowManager windowManager = getWindowManagerService();
//经过Binder调用,最终调用WMS[见小节2.8.2]
sWindowSession = windowManager.openSession(
new IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() {...},
imm.getClient(), imm.getInputContext());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
...
}
}
return sWindowSession
}
}
通过binder调用进入system_server进程,执行如下操作:
2.8.2 WMS.openSession
public IWindowSession openSession(IWindowSessionCallback callback, IInputMethodClient client,
IInputContext inputContext) {
//创建Session对象
Session session = new Session(this, callback, client, inputContext);
return session;
}
再次经过Binder将数据写回app进程,则获取的便是Session的代理对象。
2.8.3 创建对象W
[-> ViewRootImpl.java ::W]
static class W extends IWindow.Stub {
private final WeakReference<ViewRootImpl> mViewAncestor;
private final IWindowSession mWindowSession;
W(ViewRootImpl viewAncestor) {
mViewAncestor = new WeakReference<ViewRootImpl>(viewAncestor);
mWindowSession = viewAncestor.mWindowSession;
}
...
}
创建完ViewRootImpl对象后,再回到小节2.7,接下来调用该对象的setView方法。
2.9 VRI.setView
[-> ViewRootImpl.java]
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
synchronized (this) {
...
//通过Binder调用,进入system进程的Session[见小节2.10]
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(),
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mInputChannel);
...
}
}
通过Binder调用,进入system_server进程的Session对象
2.10 Session.addToDisplay
[-> Session.java]
final class Session extends IWindowSession.Stub implements IBinder.DeathRecipient {
public int addToDisplay(IWindow window, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int viewVisibility, int displayId, Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets,
Rect outOutsets, InputChannel outInputChannel) {
//[见小节2.11]
return mService.addWindow(this, window, seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId,
outContentInsets, outStableInsets, outOutsets, outInputChannel);
}
}
2.11 WMS.addWindow
[-> WindowManagerService.java]
public int addWindow(Session session, IWindow client, int seq,
WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility, int displayId,
Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets, Rect outOutsets,
InputChannel outInputChannel) {
...
WindowToken token = mTokenMap.get(attrs.token);
//创建WindowState【见小节2.11.1】
WindowState win = new WindowState(this, session, client, token,
attachedWindow, appOp[0], seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayContent);
...
//调整WindowManager的LayoutParams参数
mPolicy.adjustWindowParamsLw(win.mAttrs);
res = mPolicy.prepareAddWindowLw(win, attrs);
addWindowToListInOrderLocked(win, true);
// 设置input
mInputManager.registerInputChannel(win.mInputChannel, win.mInputWindowHandle);
//【见小节2.11.2】
win.attach();
mWindowMap.put(client.asBinder(), win);
if (win.canReceiveKeys()) {
//当该窗口能接收按键事件,则更新聚焦窗口【见小节2.12】
focusChanged = updateFocusedWindowLocked(UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_ASSIGN_LAYERS,
false /*updateInputWindows*/);
}
assignLayersLocked(displayContent.getWindowList());
...
}
2.11.1 WindowState
[-> WindowState.java]
WindowState(WindowManagerService service, Session s, IWindow c, WindowToken token,
WindowState attachedWindow, int appOp, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams a,
int viewVisibility, final DisplayContent displayContent) {
mService = service;
mSession = s; //Session的Binder服务端
mClient = c; //IWindow的Binder代理端
mToken = token;
mOwnerUid = s.mUid; //所对应app的uid
...
DeathRecipient deathRecipient = new DeathRecipient();
c.asBinder().linkToDeath(deathRecipient, 0); //app端死亡则会有死亡回调
WindowState appWin = this;
WindowToken appToken = appWin.mToken;
while (appToken.appWindowToken == null) {
WindowToken parent = mService.mTokenMap.get(appToken.token);
if (parent == null || appToken == parent) {
break;
}
appToken = parent;
}
mAppToken = appToken.appWindowToken;
//创建WindowStateAnimator对象
mWinAnimator = new WindowStateAnimator(this);
//创建InputWindowHandle对象
mInputWindowHandle = new InputWindowHandle(
mAppToken != null ? mAppToken.mInputApplicationHandle : null, this,
displayContent.getDisplayId());
}
WindowState持有远程app进程中IWindow.Stub的代理镀锡,并且注册了死亡回调,当app进程死亡则会收到相应的死亡通知。
2.11.2 WS.attach
[-> WindowState.java]
void attach() {
//【见小节2.11.3】
mSession.windowAddedLocked();
}
2.11.3 windowAddedLocked
[-> Session.java]
void windowAddedLocked() {
if (mSurfaceSession == null) {
//【见小节2.11.4】
mSurfaceSession = new SurfaceSession();
mService.mSessions.add(this);
if (mLastReportedAnimatorScale != mService.getCurrentAnimatorScale()) {
mService.dispatchNewAnimatorScaleLocked(this);
}
}
mNumWindow++;
}
创建SurfaceSession对象,并将当前Session添加到WMS.mSessions成员变量。
2.11.4 nativeCreate
[-> android_view_SurfaceSession.cpp]
static jlong nativeCreate(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz) {
SurfaceComposerClient* client = new SurfaceComposerClient();
client->incStrong((void*)nativeCreate);
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(client);
}
创建SurfaceComposerClient对象, 作为跟SurfaceFlinger通信的代理对象。
2.12 WMS.updateFocusedWindowLocked
[-> WindowManagerService.java]
private boolean updateFocusedWindowLocked(int mode, boolean updateInputWindows) {
//计算当前聚焦的窗口【见小节2.12.1】
WindowState newFocus = computeFocusedWindowLocked();
if (mCurrentFocus != newFocus) {
mH.removeMessages(H.REPORT_FOCUS_CHANGE);
mH.sendEmptyMessage(H.REPORT_FOCUS_CHANGE);
final DisplayContent displayContent = getDefaultDisplayContentLocked();
final boolean imWindowChanged = moveInputMethodWindowsIfNeededLocked(
mode != UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_ASSIGN_LAYERS
&& mode != UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_PLACE_SURFACES);
if (imWindowChanged) {
displayContent.layoutNeeded = true;
newFocus = computeFocusedWindowLocked();
}
final WindowState oldFocus = mCurrentFocus;
mCurrentFocus = newFocus;
mLosingFocus.remove(newFocus);
int focusChanged = mPolicy.focusChangedLw(oldFocus, newFocus);
if (imWindowChanged && oldFocus != mInputMethodWindow) {
//输入法窗口的焦点改变,则执行layout
if (mode == UPDATE_FOCUS_PLACING_SURFACES) {
//执行layout操作【2.13】
performLayoutLockedInner(displayContent, true /*initial*/, updateInputWindows);
focusChanged &= ~WindowManagerPolicy.FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_LAYOUT;
} else if (mode == UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_PLACE_SURFACES) {
assignLayersLocked(displayContent.getWindowList());
}
}
if ((focusChanged & WindowManagerPolicy.FINISH_LAYOUT_REDO_LAYOUT) != 0) {
displayContent.layoutNeeded = true;
if (mode == UPDATE_FOCUS_PLACING_SURFACES) {
performLayoutLockedInner(displayContent, true /*initial*/, updateInputWindows);
}
}
if (mode != UPDATE_FOCUS_WILL_ASSIGN_LAYERS) {
mInputMonitor.setInputFocusLw(mCurrentFocus, updateInputWindows);
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
这里的遍历过程:
- 从WMS.mDisplayContents中获取DisplayContent对象;
- 从DisplayContent中获取WindowList对象;
- 从WindowList中获取WindowState对象;
- 从WindowState中获取AppWindowToken对象;
mDisplayContents ->DisplayContent ->WindowList ->WindowState ->AppWindowToken.
2.12.1 WMS.computeFocusedWindowLocked
private WindowState computeFocusedWindowLocked() {
final int displayCount = mDisplayContents.size();
for (int i = 0; i < displayCount; i++) {
final DisplayContent displayContent = mDisplayContents.valueAt(i);
//【见小节2.12.2】
WindowState win = findFocusedWindowLocked(displayContent);
if (win != null) {
return win;
}
}
return null;
}
2.12.2 WMS.findFocusedWindowLocked
private WindowState findFocusedWindowLocked(DisplayContent displayContent) {
final WindowList windows = displayContent.getWindowList();
for (int i = windows.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final WindowState win = windows.get(i);
//不能接收key事件的窗口则忽略
if (!win.canReceiveKeys()) {
continue;
}
AppWindowToken wtoken = win.mAppToken;
//当窗口的app已被移除则忽略
if (wtoken != null && (wtoken.removed || wtoken.sendingToBottom)) {
continue;
}
if (wtoken != null && win.mAttrs.type != TYPE_APPLICATION_STARTING &&
mFocusedApp != null) {
ArrayList<Task> tasks = displayContent.getTasks();
for (int taskNdx = tasks.size() - 1; taskNdx >= 0; --taskNdx) {
AppTokenList tokens = tasks.get(taskNdx).mAppTokens;
int tokenNdx = tokens.size() - 1;
for ( ; tokenNdx >= 0; --tokenNdx) {
final AppWindowToken token = tokens.get(tokenNdx);
//找到聚焦窗口
if (wtoken == token) {
break;
}
if (mFocusedApp == token) {
return null;
}
}
if (tokenNdx >= 0) {
break;
}
}
}
return win;
}
return null;
}
2.13 WMS.performLayoutLockedInner
private final void performLayoutLockedInner(final DisplayContent displayContent,
boolean initial, boolean updateInputWindows) {
if (!displayContent.layoutNeeded) {
return;
}
displayContent.layoutNeeded = false;
WindowList windows = displayContent.getWindowList();
boolean isDefaultDisplay = displayContent.isDefaultDisplay;
DisplayInfo displayInfo = displayContent.getDisplayInfo();
...
final int N = windows.size();
//开始布局
mPolicy.beginLayoutLw(isDefaultDisplay, dw, dh, mRotation);
if (isDefaultDisplay) {
mSystemDecorLayer = mPolicy.getSystemDecorLayerLw();
mScreenRect.set(0, 0, dw, dh);
}
mPolicy.getContentRectLw(mTmpContentRect);
displayContent.resize(mTmpContentRect);
int seq = mLayoutSeq+1;
if (seq < 0) seq = 0;
mLayoutSeq = seq;
boolean behindDream = false;
int topAttached = -1;
for (i = N-1; i >= 0; i--) {
final WindowState win = windows.get(i);
// 当不可见或即将不可见,则不执行layout
final boolean gone = (behindDream && mPolicy.canBeForceHidden(win, win.mAttrs))
|| win.isGoneForLayoutLw();
if (!gone || !win.mHaveFrame || win.mLayoutNeeded
|| ((win.isConfigChanged() || win.setInsetsChanged()) &&
((win.mAttrs.privateFlags & PRIVATE_FLAG_KEYGUARD) != 0 ||
(win.mHasSurface && win.mAppToken != null &&
win.mAppToken.layoutConfigChanges)))) {
if (!win.mLayoutAttached) {
...
} else {
if (topAttached < 0) topAttached = i;
}
}
}
boolean attachedBehindDream = false;
//执行attach窗口的布局操作
for (i = topAttached; i >= 0; i--) {
final WindowState win = windows.get(i);
if (win.mLayoutAttached) {
if (attachedBehindDream && mPolicy.canBeForceHidden(win, win.mAttrs)) {
continue;
}
if ((win.mViewVisibility != View.GONE && win.mRelayoutCalled)
|| !win.mHaveFrame || win.mLayoutNeeded) {
if (initial) {
win.mContentChanged = false;
}
win.mLayoutNeeded = false;
win.prelayout();
mPolicy.layoutWindowLw(win, win.mAttachedWindow);
win.mLayoutSeq = seq;
}
} else if (win.mAttrs.type == TYPE_DREAM) {
attachedBehindDream = behindDream;
}
}
//窗口的帧已改变,则告知input分发器
mInputMonitor.setUpdateInputWindowsNeededLw();
if (updateInputWindows) {
mInputMonitor.updateInputWindowsLw(false /*force*/);
}
mPolicy.finishLayoutLw();
}
三. 总结
Activity的启动过程同时贯穿着AMS/WMS相关信息的创建,本文从Window角度来看待整个过程:
第一阶段运行在system_server进程:
- 将Window相应task移至顶部,并创建AppWindowToken对象,添加到WMS.mTokenMap记录该信息;
- 发送消息到”android.display”线程来处理ADD_STARTING启动窗口的消息。
第二阶段运行在目标进程的主线程:(当然在该阶段有些方法会Binder call到system_server进程)
- 创建获取AMS的binder代理;
- 执行performLaunchActivity过程,创建如下对象:
- 创建LoadedApk对象;
- 创建ComponentName对象;
- 创建目标Activity对象;
- 创建Application对象;
- 创建完Activity,执行attach操作,初始化成员变量:
- mWindow:数据类型为PhoneWindow,继承于Window对象;
- mWindowManager:数据类型为WindowManagerImpl,实现WindowManager接口;
- mToken:远程ActivityRecord的appToken的代理端
- 执行performResumeActivity过程;
- 回调onResume()方法;
- 执行addView过程:
- 创建ViewRootImpl对象;
- 创建WMS端的Session的代理对象;
- 创建继承于IWindow.Stub的ViewRootImpl.W对象;
- 执行setView()添加视图到WMS;
- 在WMS中创建WindowState对象;
- updateFocusedWindowLocked来更新聚焦窗口情况。
微信公众号 Gityuan | 微博 weibo.com/gityuan | 博客 留言区交流