基于Flutter 1.5,从源码视角来深入剖析flutter渲染机制,相关源码目录见文末附录
一、UI线程渲染
Flutter是谷歌开源的移动UI框架,可以快速在Android和iOS上构建出高质量的原生用户界面,目前全世界越来越多的开发者加入到Flutter的队伍。 Flutter相比RN性能更好,由于Flutter自己实现了一套UI框架,丢弃了原生的UI框架,非常接近原生的体验。
为了揭秘Flutter高性能,本文从源码角度来看看Flutter的渲染绘制机制,跟渲染直接相关的两个线程是UI线程和GPU线程:
- UI线程:运行着UI Task Runner,是Flutter Engine用于执行Dart root isolate代码,将其转换为layer tree视图结构;
- GPU线程:该线程依然是在CPU上执行,运行着GPU Task Runner,处理layer tree,将其转换成为GPU命令并发送到GPU。
通过VSYNC信号使UI线程和GPU线程有条不紊的周期性的渲染界面,本文介绍VSYNC的产生过程、UI线程在引擎和框架的绘制工作,下一篇文章会介绍GPU线程的绘制工作。
1.1 UI渲染原理
1.1.1 UI渲染概览
通过VSYNC信号使UI线程和GPU线程有条不紊的周期性的渲染界面,如下图所示:
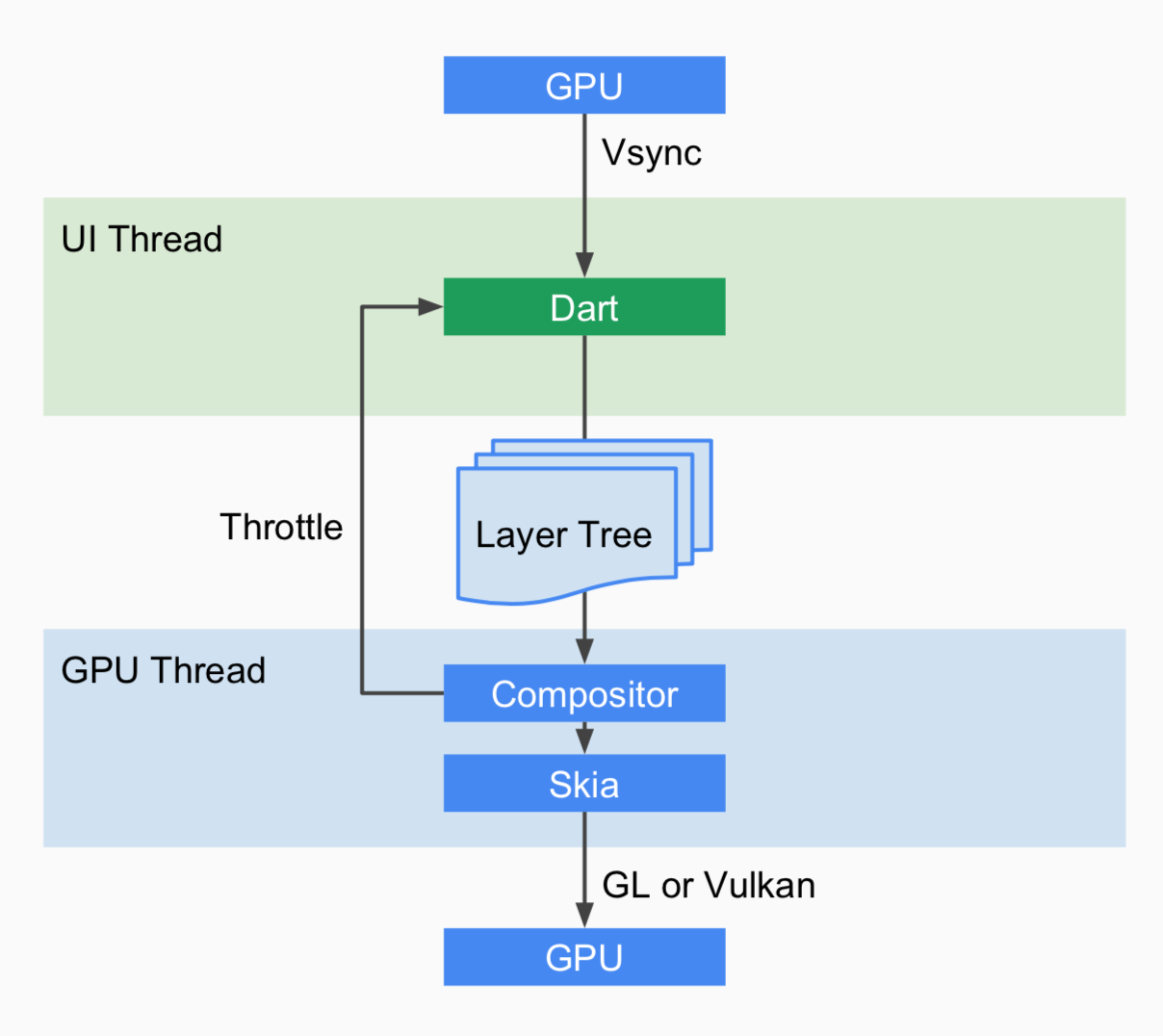
- 当需要渲染则会调用到Engine的ScheduleFrame()来注册VSYNC信号回调,一旦触发回调doFrame()执行完成后,便会移除回调方法,也就是说一次注册一次回调;
- 当需要再次绘制则需要重新调用到ScheduleFrame()方法,该方法的唯一重要参数regenerate_layer_tree决定在帧绘制过程是否需要重新生成layer tree,还是直接复用上一次的layer tree;
- UI线程的绘制过程,最核心的是执行WidgetsBinding的drawFrame()方法,然后会创建layer tree视图树
- 再交由GPU Task Runner将layer tree提供的信息转化为平台可执行的GPU指令。
1.1.2 UI绘制核心工作
1)Vsync单注册模式:保证在一帧的时间窗口里UI线程只会生成一个layer tree发送给GPU线程,原理如下:
Animator中的信号量pending_frame_semaphore_用于控制不能连续频繁地调用Vsync请求,一次只能存在Vsync注册。 pending_frame_semaphore_初始值为1,在Animator::RequestFrame()消费信号会减1,当而后再次调用则会失败直接返回; Animator的BeginFrame()或者DrawLastLayerTree()方法会执行信号加1操作。
2)UI绘制最核心的方法是drawFrame(),包含以下几个过程:
- Animate: 遍历_transientCallbacks,执行动画回调方法;
- Build: 对于dirty的元素会执行build构造,没有dirty元素则不会执行,对应于buildScope()
- Layout: 计算渲染对象的大小和位置,对应于flushLayout(),这个过程可能会嵌套再调用build操作;
- Compositing bits: 更新具有脏合成位的任何渲染对象, 对应于flushCompositingBits();
- Paint: 将绘制命令记录到Layer, 对应于flushPaint();
- Compositing: 将Compositing bits发送给GPU, 对应于compositeFrame();
- Semantics: 编译渲染对象的语义,并将语义发送给操作系统, 对应于flushSemantics()。
UI线程的耗时从doFrame(frameTimeNanos)中的frameTimeNanos为起点,以小节[4.10.6]Animator::Render()方法结束为终点, 并将结果保存到LayerTree的成员变量construction_time_,这便是UI线程的耗时时长。
1.1.3 Timeline说明
3)以上几个过程在Timeline中ui线程中都有体现,如下图所示:
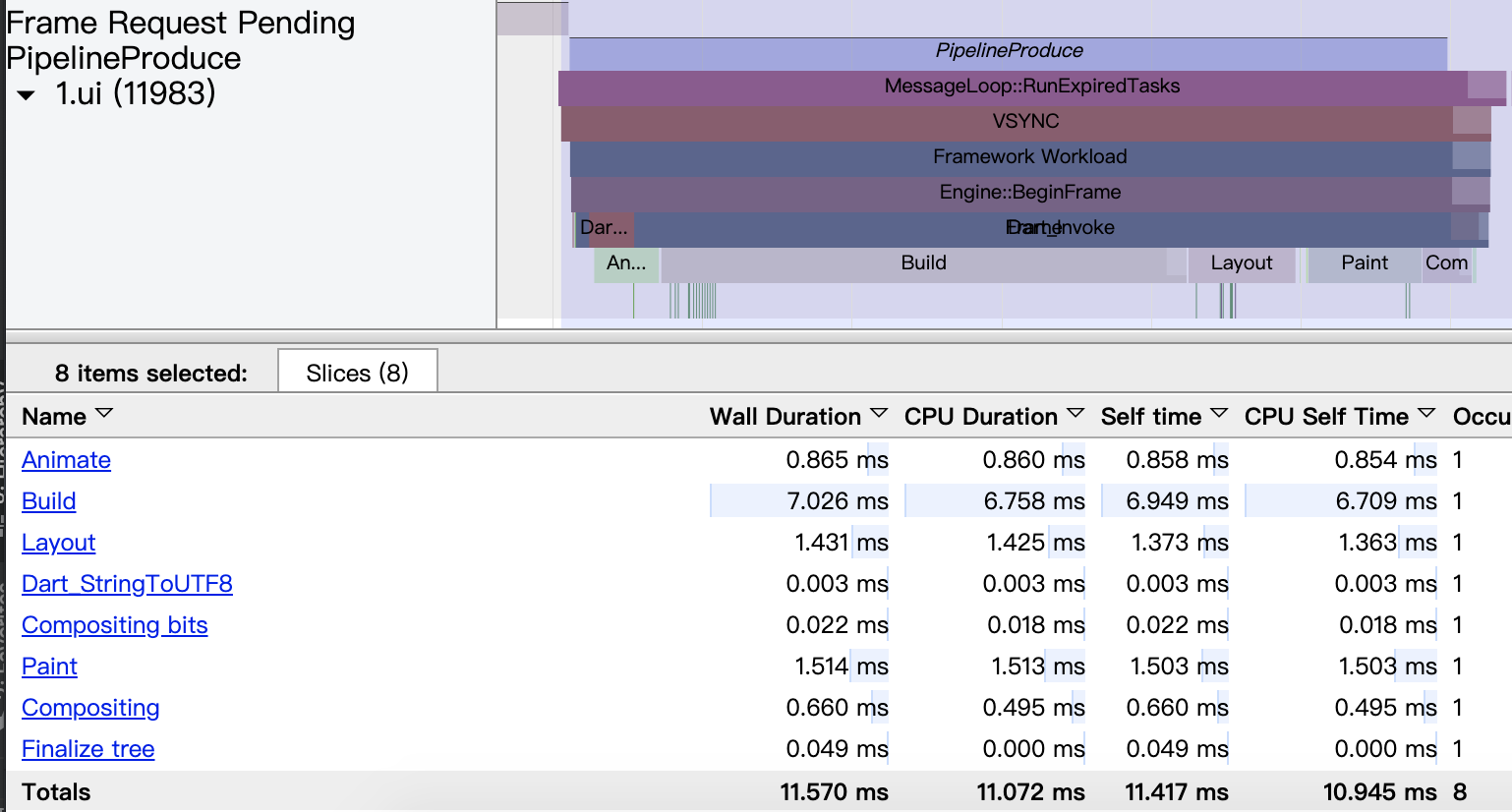
另外Timeline中还有两个比较常见的标签项
- “Frame Request Pending”:从Animator::RequestFrame 到Animator::BeginFrame()结束;
- ”PipelineProduce“: 从Animator::BeginFrame()到Animator::Render()结束。
1.2 UI线程渲染流程图
1.2.1 VSYNC注册流程
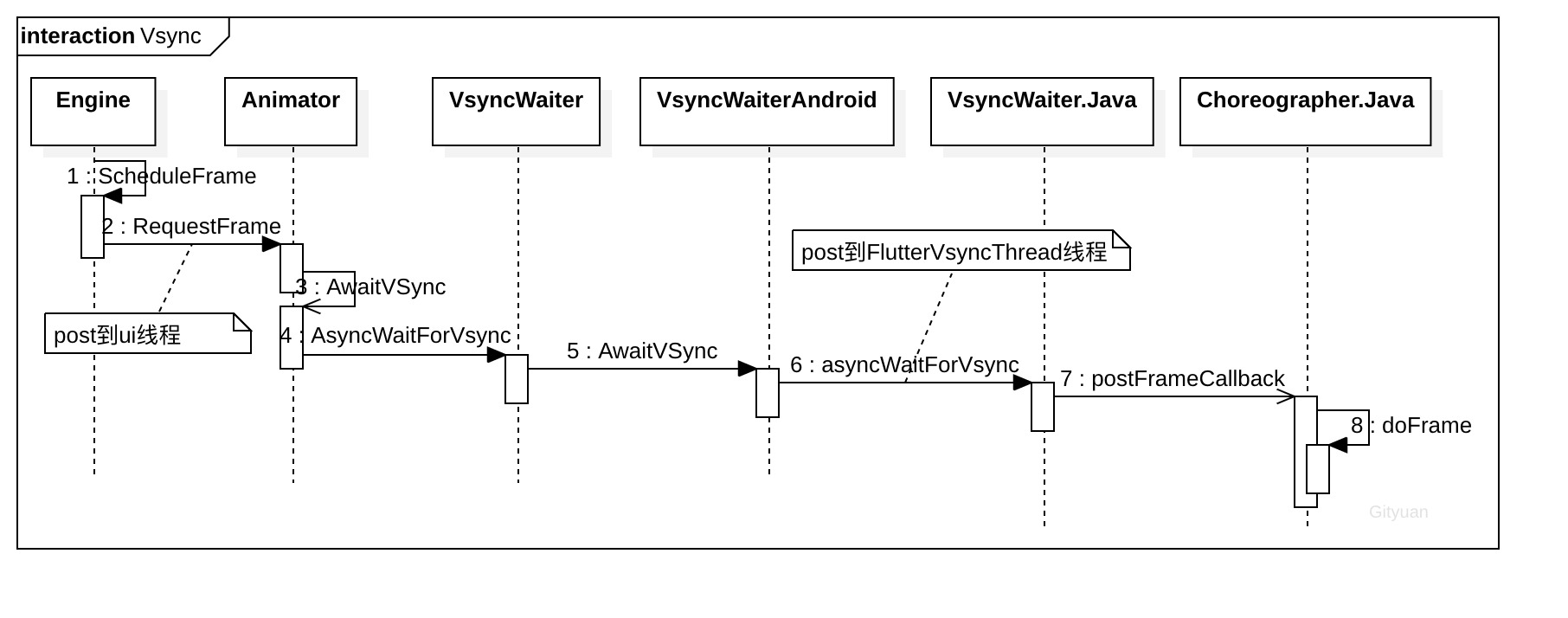
当调用到引擎Engine的ScheduleFrame()方法过程则会注册VSYNC信号回调,一旦Vsync信号达到,则会调用到doFrame()方法。 对于调用ScheduleFrame()的场景有多种,比如动画的执行AnimationController.forward(),再比如比如surface创建的时候shell::SurfaceCreated()。
1.2.2 Engine层绘制
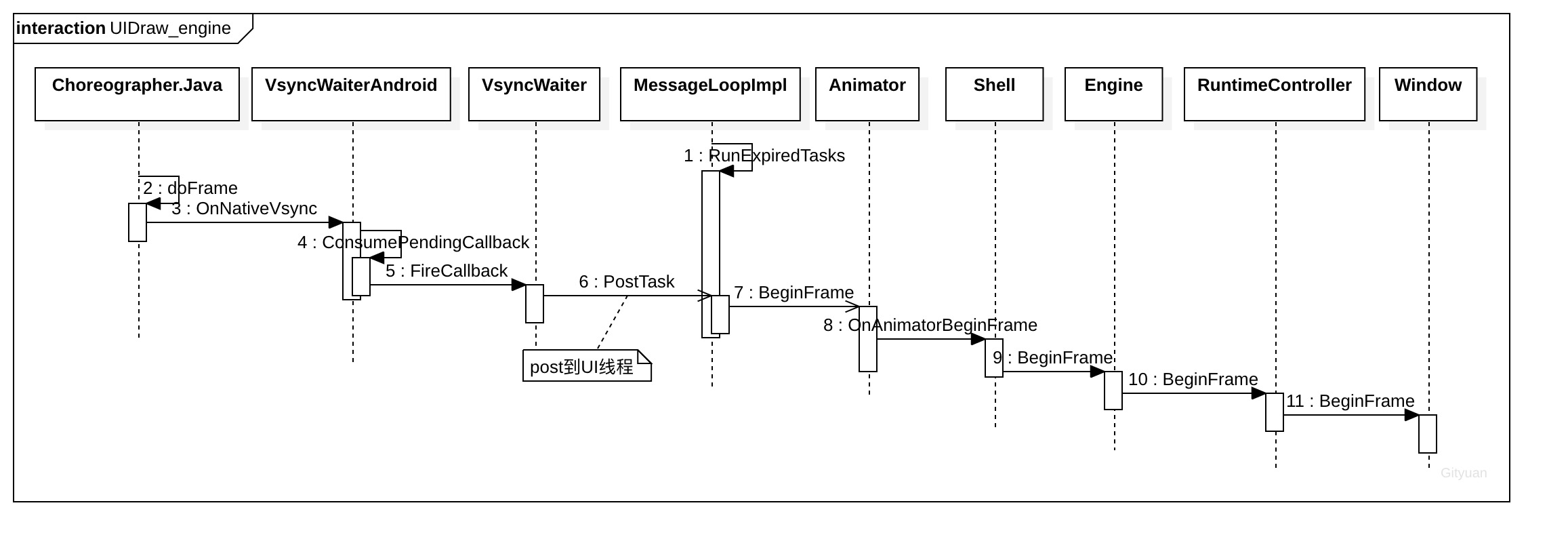
doFrame()经过多层调用后通过PostTask将任务异步post到UI TaskRunner线程来执行,最后调用到Window的BeginFrame()方法。
1.2.3 Framework层绘制
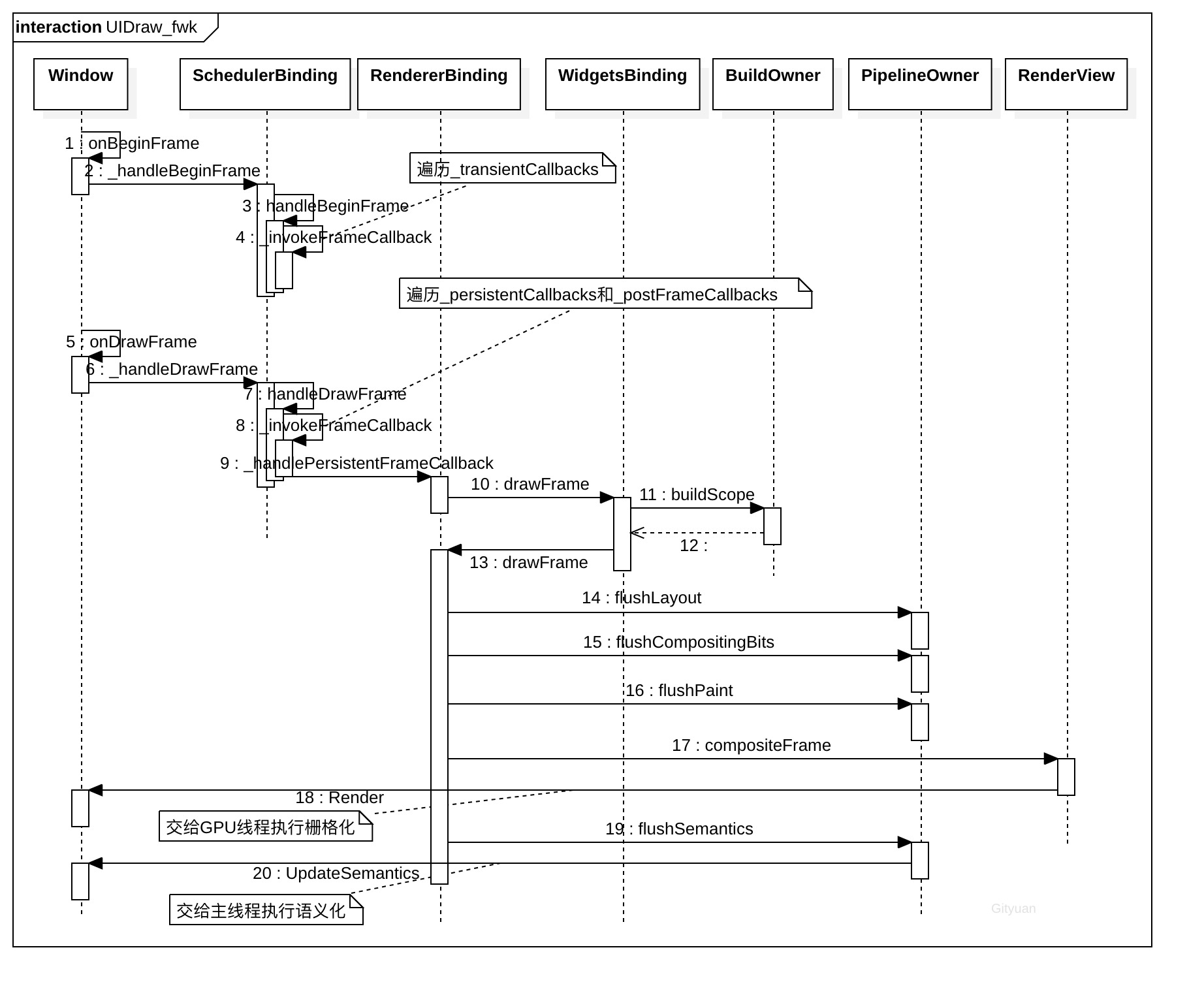
其中window.cc中的一个BeginFrame()方法,会调用到window.dart中的onBeginFrame()和onDrawFrame()两个方法。
1.3 核心类图
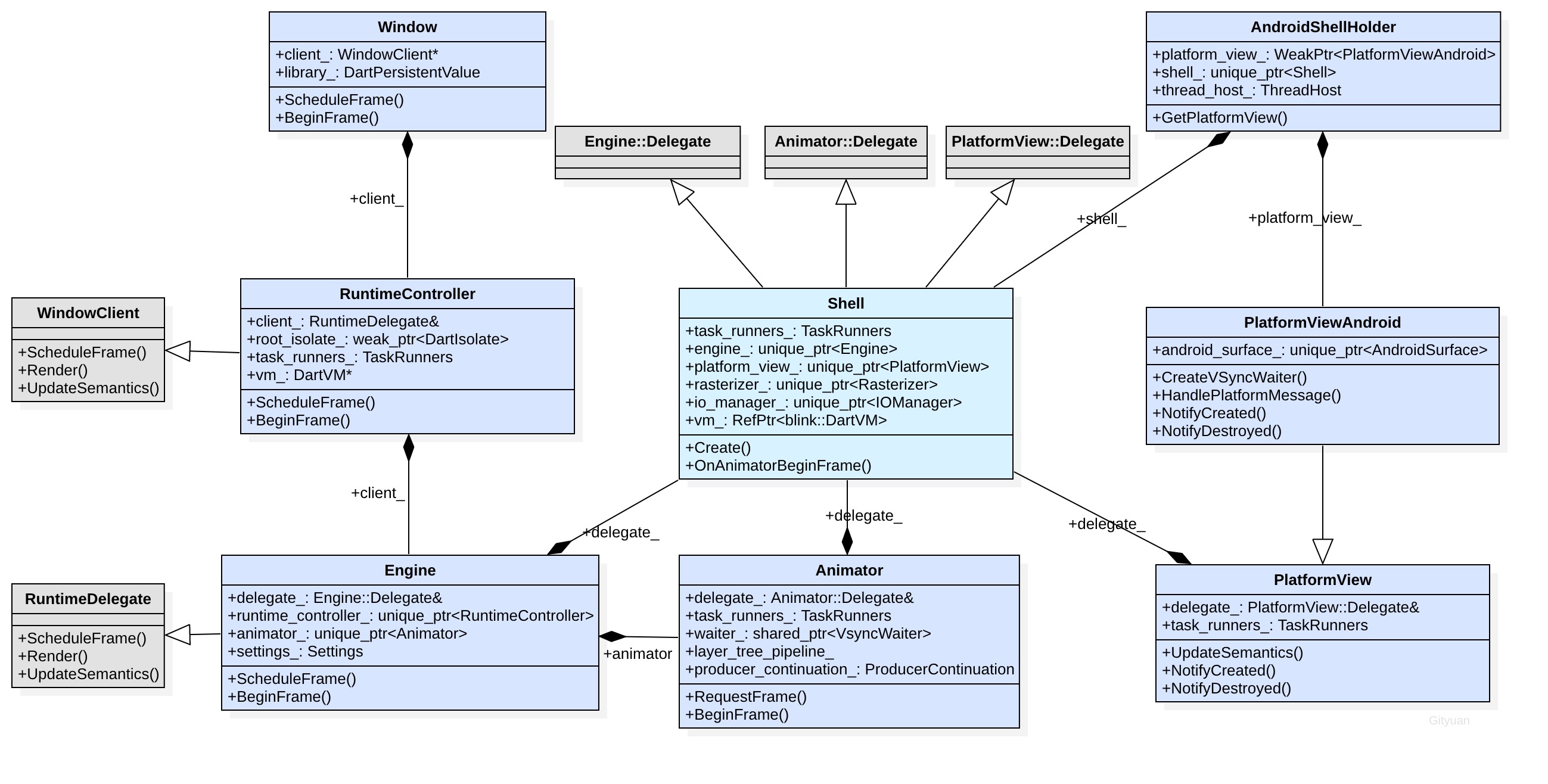
为了让大家更容易理解源码,先看一张关于Shell、Engine、Animator等Flutter等Flutter引擎中核心类的类图。
- Window类:是连接Flutter框架层(Dart)与引擎层(C++)的关键类,在框架层中window.dart文件里的一些方法在引擎层的window.cc文件有相对应的方法,比如scheduleFrame()方法。 在window.cc里面通过Window::RegisterNatives()注册了一些框架层与引擎层的方法对应关系;
- RuntimeController类:可通过其成员root_isolate_找到Window类;
- Shell类:同时继承了PlatformView::Delegate,Animator::Delegate,Engine::Delegate,所以在Engine,Animator,PlatformView中的成员变量delegate_都是指Shell对象, 从图中也能看出其中心地位,代理多项业务,该类是由AndroidShellHolder过程中初始化创建的;另外Shell类还继承了ServiceProtocol::Handler,图中省略而已。
- PlatformViewAndroid类:在Android平台上PlatformView的实例采用的便是PlatformViewAndroid类。
- Dart层与C层之间可以相互调用,从Window一路能调用到Shell类,也能从Shell类一路调用回Window。
接下来带着大家从源码角度来依次讲解Vsync注册以及UI线程的绘制处理流程,下一篇文章会介绍GPU线程的绘制工作。
二、 VSYNC注册流程
2.1 Engine::ScheduleFrame
[-> flutter/shell/common/engine.cc]
void Engine::ScheduleFrame(bool regenerate_layer_tree) {
//[见小节2.2]
animator_->RequestFrame(regenerate_layer_tree);
}
该方法说明:
- animator_的赋值过程是在Engine对象初始化过程完成,而Engine初始化过程在Shell创建过程,此处animator_便是Animator对象;
- ScheduleFrame的参数regenerate_layer_tree决定是否需要重新生成layer tree,还是直接复用上一次生成的layer tree;
- 绝大多数情况下,调用RequestFrame()时将regenerate_layer_tree_设置为true或者用默认值true,执行完Animator::BeginFrame()则设置该变量为false;
- 当无参数调用该方法时,regenerate_layer_tree为默认值为true。
- 特别的例子就是Shell::OnPlatformViewMarkTextureFrameAvailable()过程,设置参数为false,那么计划绘制一帧的时候就不需要重绘layer tree;
2.2 Animator::RequestFrame
[-> flutter/shell/common/animator.cc]
void Animator::RequestFrame(bool regenerate_layer_tree) {
if (regenerate_layer_tree) {
// regenerate_layer_tree_决定Vsync信号到来时,是否执行BeginFrame
regenerate_layer_tree_ = true;
}
//当调用Animator::Stop()则会停止动画绘制
if (paused_ && !dimension_change_pending_) {
return;
}
//调用sem_trywait来保证不会同时有多个vsync请求
if (!pending_frame_semaphore_.TryWait()) {
return;
}
task_runners_.GetUITaskRunner()->PostTask([self = weak_factory_.GetWeakPtr(),
frame_number = frame_number_]() {
if (!self.get()) {
return;
}
TRACE_EVENT_ASYNC_BEGIN0("flutter", "Frame Request Pending", frame_number);
self->AwaitVSync(); // [见小节2.3]
});
frame_scheduled_ = true; //标注已经schedule绘画帧
}
过程说明:
- pending_frame_semaphore_:非负信号量,初始值为1,第一次调用TryWait减1,而后再次调用则会失败直接返回。当消费了这次vsync回调,也就是调用了Animator的BeginFrame()或者DrawLastLayerTree()方法后,改信号量会加1[见小节3.6],可以再次执行vysnc的注册;
- 通过Animator的Start()或者BeginFrame调用到的RequestFrame方法,则肯定需要重新生成layer tree;通过Engine的ScheduleFrame方法是否重建layer tree看小节2.1;
- 此处通过post把Animator::AwaitVSync任务放入到UI Task Runner来执行。
2.3 Animator::AwaitVSync
[-> flutter/shell/common/animator.cc]
void Animator::AwaitVSync() {
// [见小节2.4]
waiter_->AsyncWaitForVsync(
[self = weak_factory_.GetWeakPtr()](fml::TimePoint frame_start_time,
fml::TimePoint frame_target_time) {
if (self) {
//是否能复用上次layer树,取决于regenerate_layer_tree_
if (self->CanReuseLastLayerTree()) {
//复用上次layer树,直接把任务post到gpu线程做栅格化操作
self->DrawLastLayerTree();
} else {
self->BeginFrame(frame_start_time, frame_target_time);
}
}
});
delegate_.OnAnimatorNotifyIdle(dart_frame_deadline_);
}
waiter_的赋值是在Animator初始化过程,取值为VsyncWaiterAndroid对象,当调用了RequestFrame(),默认参数regenerate_layer_tree_为true,意味着需要重新生成layer树,故不能重复使用上一次的layer树,接着来看一下AsyncWaitForVsync()方法的实现。
2.4 VsyncWaiter::AsyncWaitForVsync
[-> flutter/shell/common/vsync_waiter.cc]
void VsyncWaiter::AsyncWaitForVsync(Callback callback) {
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(callback_mutex_);
//赋值callback_
callback_ = std::move(callback);
}
TRACE_EVENT0("flutter", "AsyncWaitForVsync");
AwaitVSync(); // [见小节2.5]
}
此次的callback_便是[小节2.3]方法中的参数,该方法根据regenerate_layer_tree_来决定执行流。
- 当regenerate_layer_tree_=false,则执行DrawLastLayerTree();
- 当regenerate_layer_tree_=false,则执行BeginFrame();
2.5 VsyncWaiterAndroid::AwaitVSync
[-> flutter/shell/platform/android/vsync_waiter_android.cc]
void VsyncWaiterAndroid::AwaitVSync() {
std::weak_ptr<VsyncWaiter>* weak_this =
new std::weak_ptr<VsyncWaiter>(shared_from_this());
//获取VsyncWaiter的弱引用
jlong java_baton = reinterpret_cast<jlong>(weak_this);
JNIEnv* env = fml::jni::AttachCurrentThread();
// 此次调用到Java层的asyncWaitForVsync方法,java_baton指向VsyncWaiter
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(g_vsync_waiter_class->obj(), //
g_async_wait_for_vsync_method_, //
java_baton //
);
}
此处g_vsync_waiter_class,g_async_wait_for_vsync_method_的赋值过程是由JNI_OnLoad完成,如下所示。
2.5.1 JNI_OnLoad
[-> flutter/shell/platform/android/library_loader.cc]
JNIEXPORT jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM* vm, void* reserved) {
// 初始化Java虚拟机
fml::jni::InitJavaVM(vm);
JNIEnv* env = fml::jni::AttachCurrentThread();
bool result = false;
// 注册FlutterMain.
result = shell::FlutterMain::Register(env);
// 注册PlatformView [见小节2.5.2]
result = shell::PlatformViewAndroid::Register(env);
// 注册VSyncWaiter [见小节2.5.3]
result = shell::VsyncWaiterAndroid::Register(env);
return JNI_VERSION_1_4;
}
首次加载共享库时虚拟机会调用此方法。
2.5.2 Register
[-> flutter/shell/platform/android/platform_view_android_jni.cc]
bool PlatformViewAndroid::Register(JNIEnv* env) {
//记录FlutterCallbackInformation类的全局引用
g_flutter_callback_info_class = new fml::jni::ScopedJavaGlobalRef<jclass>(
env, env->FindClass("io/flutter/view/FlutterCallbackInformation"));
//记录FlutterCallbackInformation构造函数
g_flutter_callback_info_constructor = env->GetMethodID(
g_flutter_callback_info_class->obj(), "<init>",
"(Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;)V");
//记录FlutterJNI类的全局引用
g_flutter_jni_class = new fml::jni::ScopedJavaGlobalRef<jclass>(
env, env->FindClass("io/flutter/embedding/engine/FlutterJNI"));
//记录SurfaceTexture类的全局引用
g_surface_texture_class = new fml::jni::ScopedJavaGlobalRef<jclass>(
env, env->FindClass("android/graphics/SurfaceTexture"));
static const JNINativeMethod callback_info_methods[] = {
{
.name = "nativeLookupCallbackInformation",
.signature = "(J)Lio/flutter/view/FlutterCallbackInformation;",
.fnPtr = reinterpret_cast<void*>(&shell::LookupCallbackInformation),
},
};
//注册FlutterCallbackInformation的nativeLookupCallbackInformation()方法
env->RegisterNatives(g_flutter_callback_info_class->obj(),
callback_info_methods,
arraysize(callback_info_methods)) != 0);
g_is_released_method =
env->GetMethodID(g_surface_texture_class->obj(), "isReleased", "()Z");
fml::jni::ClearException(env);
g_attach_to_gl_context_method = env->GetMethodID(
g_surface_texture_class->obj(), "attachToGLContext", "(I)V");
g_update_tex_image_method =
env->GetMethodID(g_surface_texture_class->obj(), "updateTexImage", "()V");
g_get_transform_matrix_method = env->GetMethodID(
g_surface_texture_class->obj(), "getTransformMatrix", "([F)V");
g_detach_from_gl_context_method = env->GetMethodID(
g_surface_texture_class->obj(), "detachFromGLContext", "()V");
return RegisterApi(env);
}
该方法的主要工作:
- 记录和注册类FlutterCallbackInformation、FlutterJNI以及SurfaceTexture类的相关方法,用于Java和C++层方法的相互调用。
2.5.3 Register
[-> flutter/shell/platform/android/vsync_waiter_android.cc]
bool VsyncWaiterAndroid::Register(JNIEnv* env) {
static const JNINativeMethod methods[] = ;
jclass clazz = env->FindClass("io/flutter/view/VsyncWaiter");
g_vsync_waiter_class = new fml::jni::ScopedJavaGlobalRef<jclass>(env, clazz);
g_async_wait_for_vsync_method_ = env->GetStaticMethodID(
g_vsync_waiter_class->obj(), "asyncWaitForVsync", "(J)V");
return env->RegisterNatives(clazz, methods, arraysize(methods)) == 0;
}
该注册过程主要工作:
- 将Java层的VsyncWaiter类的nativeOnVsync()方法,映射到C++层的OnNativeVsync()方法,用于该方法的Java调用C++的过程;
- 将Java层的VsyncWaiter类的asyncWaitForVsync()方法,保存到C++层的g_async_wait_for_vsync_method_变量,用于该方法C++调用Java的过程。
可见,将调用VsyncWaiter类的asyncWaitForVsync()方法
2.6 asyncWaitForVsync[Java]
[-> flutter/shell/platform/android/io/flutter/view/VsyncWaiter.java]
public class VsyncWaiter {
// FlutterView的刷新时间周期(16.7ms)
public static long refreshPeriodNanos = 1000000000 / 60;
private static HandlerThread handlerThread;
private static Handler handler;
static {
handlerThread = new HandlerThread("FlutterVsyncThread");
handlerThread.start();
}
public static void asyncWaitForVsync(final long cookie) {
if (handler == null) {
handler = new Handler(handlerThread.getLooper());
}
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//注册帧回调方法,见小节[2.6.1]/[2.6.2]
Choreographer.getInstance().postFrameCallback(new Choreographer.FrameCallback() {
@Override
public void doFrame(long frameTimeNanos) {
//frameTimeNanos是VYSNC触发的时间点,也就是计划绘制的时间点
nativeOnVsync(frameTimeNanos, frameTimeNanos + refreshPeriodNanos, cookie);
}
});
}
});
}
}
通过Handler将工作post到FlutterVsyncThread线程,具体的工作是通过Choreographer来注册回调方法doFrame()以监听系统VSYNC信号。
2.6.1 Choreographer.getInstance
[-> Choreographer.java]
public static Choreographer getInstance() {
return sThreadInstance.get(); //单例模式
}
private static final ThreadLocal<Choreographer> sThreadInstance =
new ThreadLocal<Choreographer>() {
protected Choreographer initialValue() {
//获取当前线程FlutterVsyncThread的Looper
Looper looper = Looper.myLooper();
// 初始化Choreographer对象
return new Choreographer(looper);
}
};
private Choreographer(Looper looper) {
mLooper = looper;
//创建Handler对象
mHandler = new FrameHandler(looper);
//创建用于接收VSync信号的对象
mDisplayEventReceiver = USE_VSYNC ? new FrameDisplayEventReceiver(looper) : null;
mLastFrameTimeNanos = Long.MIN_VALUE; //上一次帧绘制时间点
mFrameIntervalNanos = (long)(1000000000 / getRefreshRate());
mCallbackQueues = new CallbackQueue[CALLBACK_LAST + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= CALLBACK_LAST; i++) {
mCallbackQueues[i] = new CallbackQueue();
}
}
此处Choreographer的mLooper和mHandler都运行在FlutterVsyncThread线程。
2.6.2 postFrameCallback
[-> Choreographer.java]
public void postFrameCallback(FrameCallback callback) {
postFrameCallbackDelayed(callback, 0);
}
public void postFrameCallbackDelayed(FrameCallback callback, long delayMillis) {
postCallbackDelayedInternal(CALLBACK_ANIMATION,
callback, FRAME_CALLBACK_TOKEN, delayMillis);
}
private void postCallbackDelayedInternal(int callbackType, Object action, Object token, long delayMillis) {
synchronized (mLock) {
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
final long dueTime = now + delayMillis;
//添加到mCallbackQueues队列
mCallbackQueues[callbackType].addCallbackLocked(dueTime, action, token);
if (dueTime <= now) {
scheduleFrameLocked(now);
} else {
...
}
}
}
将FrameCallback方法加入到mCallbackQueues[CALLBACK_ANIMATION]回调队列中。
三、Engine层绘制
3.1 doFrame
[-> Choreographer.java]
public void doFrame(long frameTimeNanos) {
//Android FW每次当vsync信号触发,则会调用该方法 [见下方]
nativeOnVsync(frameTimeNanos, frameTimeNanos + refreshPeriodNanos, cookie);
}
Vsync注册过程见[小节2.6] Choreographer.FrameCallback()。注册了Vysnc信号后,一旦底层Vsync信号触发,经过层层调用回到FrameDisplayEventReceiver的过程,然后会有一个通过handler的方式post到线程”FlutterVsyncThread”来执行操作, 具体流程见Choreographer原理。紧接着再处理所有注册的doCallbacks方法,则会执行Choreographer.FrameCallback中的doFrame()方法,如下所示。
new Choreographer.FrameCallback() {
@Override
public void doFrame(long frameTimeNanos) {
//frameTimeNanos是VYSNC触发的时间点,也就是计划绘制的时间点 [见小节3.2]
nativeOnVsync(frameTimeNanos, frameTimeNanos + refreshPeriodNanos, cookie);
}
}
3.2 OnNativeVsync
[-> flutter/shell/platform/android/io/flutter/view/VsyncWaiter.java]
public class VsyncWaiter {
...
// [见小节3.2.1]
private static native void nativeOnVsync(long frameTimeNanos,
long frameTargetTimeNanos,
long cookie);
...
}
由[小节2.5.3]可知,VsyncWaiter.java中的nativeOnVsync对应于vsync_waiter_android.cc的OnNativeVsync(),具体过程在jni加载过程初始化,如下所示。
3.2.1 OnNativeVsync[C++]
[-> flutter/shell/platform/android/vsync_waiter_android.cc]
static void OnNativeVsync(JNIEnv* env, jclass jcaller,
jlong frameTimeNanos,
jlong frameTargetTimeNanos,
jlong java_baton) {
auto frame_time = fml::TimePoint::FromEpochDelta(
fml::TimeDelta::FromNanoseconds(frameTimeNanos));
auto target_time = fml::TimePoint::FromEpochDelta(
fml::TimeDelta::FromNanoseconds(frameTargetTimeNanos));
//消费pending回调[见小节3.3]
ConsumePendingCallback(java_baton, frame_time, target_time);
}
3.3 ConsumePendingCallback
[-> flutter/shell/platform/android/vsync_waiter_android.cc]
static void ConsumePendingCallback(jlong java_baton,
fml::TimePoint frame_start_time,
fml::TimePoint frame_target_time) {
auto* weak_this = reinterpret_cast<std::weak_ptr<VsyncWaiter>*>(java_baton);
auto shared_this = weak_this->lock();
delete weak_this;
if (shared_this) {
//shared_this指向VsyncWaiter的弱引用 [见小节3.4]
shared_this->FireCallback(frame_start_time, frame_target_time);
}
}
3.4 VsyncWaiter::FireCallback
[-> flutter/shell/common/vsync_waiter.cc]
void VsyncWaiter::FireCallback(fml::TimePoint frame_start_time,
fml::TimePoint frame_target_time) {
Callback callback;
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(callback_mutex_);
callback = std::move(callback_);
}
if (!callback) {
TRACE_EVENT_INSTANT0("flutter", "MismatchedFrameCallback");
return;
}
TRACE_EVENT0("flutter", "VsyncFireCallback");
//将任务放入task队列[见小节3.4.1]
task_runners_.GetUITaskRunner()->PostTaskForTime(
[callback, flow_identifier, frame_start_time, frame_target_time]() {
FML_TRACE_EVENT("flutter", kVsyncTraceName, "StartTime",
frame_start_time, "TargetTime", frame_target_time);
fml::tracing::TraceEventAsyncComplete(
"flutter", "VsyncSchedulingOverhead", fml::TimePoint::Now(),
frame_start_time);
//开始执行vync [见小节3.5]
callback(frame_start_time, frame_target_time);
TRACE_FLOW_END("flutter", kVsyncFlowName, flow_identifier);
},
frame_start_time);
}
将任务闭包放入task队列,消息Loop一旦接受到消息则会读取出来。
3.4.1 MessageLoopImpl::RunExpiredTasks
[-> flutter/fml/message_loop_impl.cc]
void MessageLoopImpl::RunExpiredTasks() {
TRACE_EVENT0("fml", "MessageLoop::RunExpiredTasks");
std::vector<fml::closure> invocations;
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(delayed_tasks_mutex_);
//当没有待处理的task则直接返回
if (delayed_tasks_.empty()) {
return;
}
auto now = fml::TimePoint::Now();
while (!delayed_tasks_.empty()) {
const auto& top = delayed_tasks_.top();
if (top.target_time > now) {
break;
}
invocations.emplace_back(std::move(top.task));
delayed_tasks_.pop();
}
WakeUp(delayed_tasks_.empty() ? fml::TimePoint::Max()
: delayed_tasks_.top().target_time);
}
for (const auto& invocation : invocations) {
invocation(); // [见小节3.5]
for (const auto& observer : task_observers_) {
observer.second();
}
}
}
对于ui线程处于消息loop状态,一旦有时间到达的任务则开始执行,否则处于空闲等等状态。前面[小节3.4] VsyncWaiter::FireCallback过程已经向该ui线程postTask。 对于不可复用layer tree的情况则调用Animator::BeginFrame()方法。
3.5 callback
[-> flutter/shell/common/animator.cc]
[self = weak_factory_.GetWeakPtr()](fml::TimePoint frame_start_time,
fml::TimePoint frame_target_time) {
if (self) {
if (self->CanReuseLastLayerTree()) {
self->DrawLastLayerTree();
} else {
//根据默认参数regenerate_layer_tree_为true,则执行该分支 [见小节3.6]
self->BeginFrame(frame_start_time, frame_target_time);
}
}
}
此次的callback赋值过程位于[小节2.3]Animator::AwaitVSync()方法的闭包参数,相关说明:
- frame_start_time:计划开始绘制时间点,来源于doFrame()方法中的参数;
- frame_target_time:从frame_start_time加上一帧时间(16.7ms)的时间,作为本次绘制的deadline。
3.6 Animator::BeginFrame
[-> flutter/shell/common/animator.cc]
void Animator::BeginFrame(fml::TimePoint frame_start_time,
fml::TimePoint frame_target_time) {
TRACE_EVENT_ASYNC_END0("flutter", "Frame Request Pending", frame_number_++);
TRACE_EVENT0("flutter", "Animator::BeginFrame");
frame_scheduled_ = false;
notify_idle_task_id_++;
regenerate_layer_tree_ = false;
//信号量加1,可以注册新的vsync信号,也就是能执行Animator::RequestFrame()
pending_frame_semaphore_.Signal();
if (!producer_continuation_) {
//[小节3.6.1]/[小节3.6.2]
producer_continuation_ = layer_tree_pipeline_->Produce();
//pipeline已满,说明GPU线程繁忙,则结束本次UI绘制,重新注册Vsync
if (!producer_continuation_) {
RequestFrame();
return;
}
}
//从pipeline中获取有效的continuation,并准备为可能的frame服务
last_begin_frame_time_ = frame_start_time;
//获取当前帧绘制截止时间,用于告知可GC的空闲时长
dart_frame_deadline_ = FxlToDartOrEarlier(frame_target_time);
{
TRACE_EVENT2("flutter", "Framework Workload", "mode", "basic", "frame",
FrameParity());
//此处delegate_为Shell [小节3.7]
delegate_.OnAnimatorBeginFrame(last_begin_frame_time_);
}
if (!frame_scheduled_) {
task_runners_.GetUITaskRunner()->PostDelayedTask(
[self = weak_factory_.GetWeakPtr(),
notify_idle_task_id = notify_idle_task_id_]() {
if (!self.get()) {
return;
}
// 该任务id和当前任务id一致,则不再需要审查frame,可以通知引擎当前处于空闲状态,100ms
if (notify_idle_task_id == self->notify_idle_task_id_) {
self->delegate_.OnAnimatorNotifyIdle(Dart_TimelineGetMicros() +
100000);
}
},
kNotifyIdleTaskWaitTime); //延迟51ms再通知引擎空闲状态
}
}
该方法主要功能说明:
- layer_tree_pipeline_是在Animator对象初始化的过程中创建的LayerTreePipeline,其类型为Pipeline
- 此处kNotifyIdleTaskWaitTime等于51ms,等于3帧的时间+1ms,之所以这样设计是由于在某些工作负载下(比如父视图调整大小,通过viewport metrics事件传达给子视图)实际上还没有schedule帧,尽管在下一个vsync会生成一帧(将在收到viewport事件后schedule),因此推迟调用OnAnimatorNotifyIdle一点点,从而避免可能垃圾回收在不希望的时间触发。
3.6.1 LayerTreePipeline初始化
[-> flutter/shell/common/animator.cc]
Animator::Animator(Delegate& delegate,
TaskRunners task_runners,
std::unique_ptr<VsyncWaiter> waiter)
: delegate_(delegate),
task_runners_(std::move(task_runners)),
waiter_(std::move(waiter)),
last_begin_frame_time_(),
dart_frame_deadline_(0),
layer_tree_pipeline_(fml::MakeRefCounted<LayerTreePipeline>(2)),
... {}
此处LayerTreePipeline的初始化过程如下:
using LayerTreePipeline = Pipeline<flutter::LayerTree>;
在pipeline.h的过程会初始化Pipeline,可见初始值empty_ = 2,available_ = 0;
Pipeline(uint32_t depth) : empty_(depth), available_(0) {}
3.6.2 Pipeline::Produce
[-> flutter/synchronization/pipeline.h]
ProducerContinuation Produce() {
//当管道不为空,则不允许再次向管道加入数据
if (!empty_.TryWait()) {
return {};
}
//[见小节3.6.3]
return ProducerContinuation{
std::bind(&Pipeline::ProducerCommit, this, std::placeholders::_1,
std::placeholders::_2), // continuation
GetNextPipelineTraceID()};
}
通过信号量empty_的初始值为depth(默认等于2),来保证同一个管道的任务最多不超过depth个,每次UI线程执行Produce()会减1,当GPU线程执行完成Consume()方法后才会执行加1操作。
3.6.3 ProducerContinuation初始化
[-> flutter/synchronization/pipeline.h]
ProducerContinuation(Continuation continuation, size_t trace_id)
: continuation_(continuation), trace_id_(trace_id) {
TRACE_FLOW_BEGIN("flutter", "PipelineItem", trace_id_);
TRACE_EVENT_ASYNC_BEGIN0("flutter", "PipelineProduce", trace_id_);
}
3.6.3 Pipeline.ProducerCommit
[-> flutter/synchronization/pipeline.h]
void ProducerCommit(ResourcePtr resource, size_t trace_id) {
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(queue_mutex_);
queue_.emplace(std::move(resource), trace_id);
}
available_.Signal();
}
3.7 Shell::OnAnimatorBeginFrame
[-> flutter/shell/common/shell.cc]
void Shell::OnAnimatorBeginFrame(fml::TimePoint frame_time) {
if (engine_) {
engine_->BeginFrame(frame_time); // [小节3.8]
}
}
3.8 Engine::BeginFrame
[-> flutter/shell/common/engine.cc]
void Engine::BeginFrame(fml::TimePoint frame_time) {
TRACE_EVENT0("flutter", "Engine::BeginFrame");
runtime_controller_->BeginFrame(frame_time); // [小节3.9]
}
3.9 RuntimeController::BeginFrame
[-> flutter/runtime/runtime_controller.cc]
bool RuntimeController::BeginFrame(fml::TimePoint frame_time) {
if (auto* window = GetWindowIfAvailable()) {
window->BeginFrame(frame_time); // [小节3.10]
return true;
}
return false;
}
3.10 Window::BeginFrame
[-> flutter/lib/ui/window/window.cc]
void Window::BeginFrame(fml::TimePoint frameTime) {
std::shared_ptr<tonic::DartState> dart_state = library_.dart_state().lock();
if (!dart_state)
return;
tonic::DartState::Scope scope(dart_state);
//注意此处的frameTime便是前面小节3.1中doFrame方法中的参数frameTimeNanos
int64_t microseconds = (frameTime - fml::TimePoint()).ToMicroseconds();
// [见小节4.2]
DartInvokeField(library_.value(), "_beginFrame",
{Dart_NewInteger(microseconds)});
//执行MicroTask
UIDartState::Current()->FlushMicrotasksNow();
// [见小节4.4]
DartInvokeField(library_.value(), "_drawFrame", {});
}
Window::BeginFrame()过程主要工作:
- 执行_beginFrame
- 执行FlushMicrotasksNow
- 执行_drawFrame
可见,Microtask位于beginFrame和drawFrame之间,那么Microtask的耗时会影响ui绘制过程。
DartInvokeField()通过dart虚拟机调用了window.onBeginFrame()和onDrawFrame方法,见hooks.dart文件中如下过程:
@pragma('vm:entry-point')
void _beginFrame(int microseconds) {
_invoke1<Duration>(window.onBeginFrame, window._onBeginFrameZone, new Duration(microseconds: microseconds));
}
@pragma('vm:entry-point')
void _drawFrame() {
_invoke(window.onDrawFrame, window._onDrawFrameZone);
}
四、Framework层绘制
在引擎层的处理过程会调用到window.onBeginFrame()和onDrawFrame,回到framework层从这个两个方法开始说起。
4.1 SchedulerBinding.initInstances
[-> lib/src/scheduler/binding.dart:: SchedulerBinding]
mixin SchedulerBinding on BindingBase, ServicesBinding {
@override
void initInstances() {
super.initInstances();
_instance = this;
ui.window.onBeginFrame = _handleBeginFrame; //[见小节4.2]
ui.window.onDrawFrame = _handleDrawFrame; //[见小节4.4]
SystemChannels.lifecycle.setMessageHandler(_handleLifecycleMessage);
}
}
可见,引擎层中的Window::BeginFrame()调用的两个方法,进入到dart层则分别是_handleBeginFrame()和_handleDrawFrame()方法
4.1.1 Window初始化
[-> flutter/lib/ui/window.dart]
class Window {
Window._()
FrameCallback get onBeginFrame => _onBeginFrame;
FrameCallback _onBeginFrame;
VoidCallback get onDrawFrame => _onDrawFrame;
VoidCallback _onDrawFrame;
...
}
Window初始化过程,可以知道onBeginFrame和onDrawFrame分别保存_onBeginFrame和_onDrawFrame方法。
4.2 _handleBeginFrame
[-> lib/src/scheduler/binding.dart:: SchedulerBinding]
void _handleBeginFrame(Duration rawTimeStamp) {
if (_warmUpFrame) {
_ignoreNextEngineDrawFrame = true;
return;
}
handleBeginFrame(rawTimeStamp); //[见小节4.3]
}
4.3 handleBeginFrame
[-> lib/src/scheduler/binding.dart:: SchedulerBinding]
void handleBeginFrame(Duration rawTimeStamp) {
Timeline.startSync('Frame', arguments: timelineWhitelistArguments);
_firstRawTimeStampInEpoch ??= rawTimeStamp;
_currentFrameTimeStamp = _adjustForEpoch(rawTimeStamp ?? _lastRawTimeStamp);
if (rawTimeStamp != null)
_lastRawTimeStamp = rawTimeStamp;
profile(() {
_profileFrameNumber += 1;
_profileFrameStopwatch.reset();
_profileFrameStopwatch.start();
});
//此时阶段等于SchedulerPhase.idle;
_hasScheduledFrame = false;
try {
Timeline.startSync('Animate', arguments: timelineWhitelistArguments);
_schedulerPhase = SchedulerPhase.transientCallbacks;
//执行动画的回调方法
final Map<int, _FrameCallbackEntry> callbacks = _transientCallbacks;
_transientCallbacks = <int, _FrameCallbackEntry>{};
callbacks.forEach((int id, _FrameCallbackEntry callbackEntry) {
if (!_removedIds.contains(id))
_invokeFrameCallback(callbackEntry.callback, _currentFrameTimeStamp, callbackEntry.debugStack);
});
_removedIds.clear();
} finally {
_schedulerPhase = SchedulerPhase.midFrameMicrotasks;
}
}
该方法主要功能是遍历_transientCallbacks,执行相应的Animate操作,可通过scheduleFrameCallback()/cancelFrameCallbackWithId()来完成添加和删除成员,再来简单看看这两个方法。
4.3.1 scheduleFrameCallback
[-> lib/src/scheduler/binding.dart:: SchedulerBinding]
int scheduleFrameCallback(FrameCallback callback, { bool rescheduling = false }) {
scheduleFrame(); //触发帧绘制的调度
_nextFrameCallbackId += 1;
_transientCallbacks[_nextFrameCallbackId] = _FrameCallbackEntry(callback, rescheduling: rescheduling);
return _nextFrameCallbackId;
}
callback保存在_FrameCallbackEntry对象里面
4.3.2 cancelFrameCallbackWithId
[-> lib/src/scheduler/binding.dart:: SchedulerBinding]
void cancelFrameCallbackWithId(int id) {
assert(id > 0);
_transientCallbacks.remove(id);
_removedIds.add(id);
}
4.4 _handleDrawFrame
[-> lib/src/scheduler/binding.dart:: SchedulerBinding]
void _handleDrawFrame() {
if (_ignoreNextEngineDrawFrame) {
_ignoreNextEngineDrawFrame = false;
return;
}
handleDrawFrame(); //[见小节4.5]
}
4.5 handleDrawFrame
[-> lib/src/scheduler/binding.dart:: SchedulerBinding]
void handleDrawFrame() {
assert(_schedulerPhase == SchedulerPhase.midFrameMicrotasks);
Timeline.finishSync(); // 标识结束"Animate"阶段
try {
_schedulerPhase = SchedulerPhase.persistentCallbacks;
//执行PERSISTENT FRAME回调
for (FrameCallback callback in _persistentCallbacks)
_invokeFrameCallback(callback, _currentFrameTimeStamp); //[见小节4.5.1]
_schedulerPhase = SchedulerPhase.postFrameCallbacks;
// 执行POST-FRAME回调
final List<FrameCallback> localPostFrameCallbacks = List<FrameCallback>.from(_postFrameCallbacks);
_postFrameCallbacks.clear();
for (FrameCallback callback in localPostFrameCallbacks)
_invokeFrameCallback(callback, _currentFrameTimeStamp);
} finally {
_schedulerPhase = SchedulerPhase.idle;
Timeline.finishSync(); //标识结束”Frame“阶段
profile(() {
_profileFrameStopwatch.stop();
_profileFramePostEvent();
});
_currentFrameTimeStamp = null;
}
}
该方法主要功能:
- 遍历_persistentCallbacks,执行相应的回调方法,可通过addPersistentFrameCallback()注册,一旦注册后不可移除,后续每一次frame回调都会执行;
- 遍历_postFrameCallbacks,执行相应的回调方法,可通过addPostFrameCallback()注册,handleDrawFrame()执行完成后会清空_postFrameCallbacks内容。
4.5.1 _invokeFrameCallback
[-> lib/src/scheduler/binding.dart:: SchedulerBinding]
void _invokeFrameCallback(FrameCallback callback, Duration timeStamp, [ StackTrace callbackStack ]) {
try {
callback(timeStamp); //[见小节4.5.2]
} catch (exception, exceptionStack) {
FlutterError.reportError(FlutterErrorDetails(...));
}
}
这里的callback是_persistentCallbacks列表中的成员,再来看看其成员是如何添加进去的。
4.5.2 WidgetsBinding.initInstances
[-> lib/src/widgets/binding.dart]
mixin WidgetsBinding on BindingBase, SchedulerBinding, GestureBinding, RendererBinding, SemanticsBinding {
@override
void initInstances() {
super.initInstances(); //[见小节4.5.3]
_instance = this;
buildOwner.onBuildScheduled = _handleBuildScheduled;
ui.window.onLocaleChanged = handleLocaleChanged;
ui.window.onAccessibilityFeaturesChanged = handleAccessibilityFeaturesChanged;
SystemChannels.navigation.setMethodCallHandler(_handleNavigationInvocation);
SystemChannels.system.setMessageHandler(_handleSystemMessage);
}
}
在flutter app启动过程,也就是执行runApp过程会有WidgetsFlutterBinding初始化过程,WidgetsBinding的initInstances(),根据mixin的顺序,可知此处的super.initInstances() 便是RendererBinding类。
4.5.3 RendererBinding.initInstances
[-> lib/src/rendering/binding.dart]
mixin RendererBinding on BindingBase, ServicesBinding, SchedulerBinding, SemanticsBinding, HitTestable {
void initInstances() {
super.initInstances();
_instance = this;
_pipelineOwner = PipelineOwner(
onNeedVisualUpdate: ensureVisualUpdate,
onSemanticsOwnerCreated: _handleSemanticsOwnerCreated,
onSemanticsOwnerDisposed: _handleSemanticsOwnerDisposed,
);
ui.window
..onMetricsChanged = handleMetricsChanged
..onTextScaleFactorChanged = handleTextScaleFactorChanged
..onSemanticsEnabledChanged = _handleSemanticsEnabledChanged
..onSemanticsAction = _handleSemanticsAction;
initRenderView();
_handleSemanticsEnabledChanged();
addPersistentFrameCallback(_handlePersistentFrameCallback); //[见小节4.5.4]
}
void _handlePersistentFrameCallback(Duration timeStamp) {
drawFrame(); //[见小节4.6]
}
}
4.5.4 SchedulerBinding.addPersistentFrameCallback
[-> lib/src/scheduler/binding.dart]
mixin SchedulerBinding on BindingBase, ServicesBinding {
void addPersistentFrameCallback(FrameCallback callback) {
_persistentCallbacks.add(callback);
}
}
4.6 WidgetsBinding.drawFrame
[-> lib/src/widgets/binding.dart]
void drawFrame() {
try {
if (renderViewElement != null)
buildOwner.buildScope(renderViewElement); //[见小节4.6.1]
super.drawFrame(); //[见小节4.6.4]
buildOwner.finalizeTree(); //[见小节4.12]
} finally {
}
}
4.6.1 BuildOwner.buildScope
[-> lib/src/widgets/framework.dart]
void buildScope(Element context, [VoidCallback callback]) {
if (callback == null && _dirtyElements.isEmpty)
return;
Timeline.startSync('Build', arguments: timelineWhitelistArguments);
try {
_scheduledFlushDirtyElements = true;
if (callback != null) {
_dirtyElementsNeedsResorting = false;
callback(); //执行回调方法
}
_dirtyElements.sort(Element._sort); //排序
_dirtyElementsNeedsResorting = false;
int dirtyCount = _dirtyElements.length;
int index = 0;
while (index < dirtyCount) {
try {
//具体Element子类执行重建操作 [见小节4.6.2]
_dirtyElements[index].rebuild();
} catch (e, stack) {
}
index += 1;
if (dirtyCount < _dirtyElements.length || _dirtyElementsNeedsResorting) {
_dirtyElements.sort(Element._sort);
_dirtyElementsNeedsResorting = false;
dirtyCount = _dirtyElements.length;
while (index > 0 && _dirtyElements[index - 1].dirty) {
index -= 1;
}
}
}
} finally {
for (Element element in _dirtyElements) {
element._inDirtyList = false;
}
_dirtyElements.clear();
_scheduledFlushDirtyElements = false;
_dirtyElementsNeedsResorting = null;
Timeline.finishSync();
}
}
4.6.2 Element.rebuild
[-> lib/src/widgets/framework.dart]
void rebuild() {
if (!_active || !_dirty)
return;
performRebuild();
}
performRebuild具体执行方法,取决于相应的Element子类,这里以ComponentElement为例
4.6.3 ComponentElement.performRebuild
[-> lib/src/widgets/framework.dart]
void performRebuild() {
Widget built;
try {
built = build(); //执行build方法
} catch (e, stack) {
built = ErrorWidget.builder(_debugReportException('building $this', e, stack));
} finally {
_dirty = false;
}
try {
_child = updateChild(_child, built, slot); //更新子元素
} catch (e, stack) {
built = ErrorWidget.builder(_debugReportException('building $this', e, stack));
_child = updateChild(null, built, slot);
}
}
4.6.4 RendererBinding.drawFrame
[-> lib/src/rendering/binding.dart]
void drawFrame() {
pipelineOwner.flushLayout(); //[见小节4.7]
pipelineOwner.flushCompositingBits(); //[见小节4.8]
pipelineOwner.flushPaint(); //[见小节4.9]
renderView.compositeFrame(); //[见小节4.10]
pipelineOwner.flushSemantics(); //[见小节4.11]
}
RendererBinding的initInstances()过程注册了一个Persistent的帧回调方法_handlePersistentFrameCallback(),故handleDrawFrame()过程会调用该方法。pipelineOwner管理渲染管道,提供了一个用于驱动渲染管道的接口,并存储了哪些渲染对象请求访问状态,要刷新管道,需要按顺序运行如下5个阶段:
- [flushLayout]:更新需要计算其布局的渲染对象,在此阶段计算每个渲染对象的大小和位置,渲染对象可能会弄脏其绘画或者合成状态,这个过程可能还会调用到build过程。
- 耗时对应timeline的‘Layout’过程
- [flushCompositingBits]:更新具有脏合成位的任何渲染对象,在此阶段每个渲染对象都会了解其子项是否需要合成。在绘制阶段使用此信息选择如何实现裁剪等视觉效果。如果渲染对象有一个自己合成的子项,它需要使用布局信息来创建裁剪,以便将裁剪应用于已合成的子项
- 耗时对应timeline的‘Compositing bits’过程
- [flushPaint]:访问需要绘制的任何渲染对象,在此阶段,渲染对象有机会将绘制命令记录到[PictureLayer],并构建其他合成的[Layer];
- 耗时对应timeline的‘Paint’过程
- [compositeFrame]:将Compositing bits发送给GPU;
- 耗时对应timeline的‘Compositing’过程
- [flushSemantics]:编译渲染对象的语义,并将语义发送给操作系统;
- 耗时对应timeline的‘Semantics’过程
packages/flutter/lib/src/rendering/debug.dart,这里面记录着关于render过程相关的调试开关,可以逐一实践。
4.7 PipelineOwner.flushLayout
[-> lib/src/rendering/object.dart]
void flushLayout() {
profile(() {
Timeline.startSync('Layout', arguments: timelineWhitelistArguments);
});
try {
//遍历所有的渲染对象
while (_nodesNeedingLayout.isNotEmpty) {
final List<RenderObject> dirtyNodes = _nodesNeedingLayout;
_nodesNeedingLayout = <RenderObject>[];
for (RenderObject node in dirtyNodes..sort((RenderObject a, RenderObject b) => a.depth - b.depth)) {
//如果渲染对象需要重新布局,则执行布局操作 [见小节4.7.1]
if (node._needsLayout && node.owner == this)
node._layoutWithoutResize();
}
}
} finally {
profile(() {
Timeline.finishSync();
});
}
}
4.7.1 _layoutWithoutResize
[-> lib/src/rendering/object.dart]
void _layoutWithoutResize() {
try {
performLayout(); //执行布局操作[]
markNeedsSemanticsUpdate(); //[见小节4.7.2]
} catch (e, stack) {
_debugReportException('performLayout', e, stack);
}
_needsLayout = false; //完成layout操作
markNeedsPaint(); // [见小节4.7.3]
}
该方法主要工作:
- performLayout操作:参数sizedByParent为false需要同时改变渲染对象和指导子项的布局,性能更慢;
- markNeedsSemanticsUpdate:标记需要更新语义;
- markNeedsPaint:标记需要绘制;
SchedulerBinding.scheduleWarmUpFrame
RenderView.performLayout
RenderObject.layout
_RenderLayoutBuilder.performLayout
_LayoutBuilderElement._layout
BuildOwner.buildScope
4.7.2 markNeedsSemanticsUpdate
[-> lib/src/rendering/object.dart]
void markNeedsSemanticsUpdate() {
if (!attached || owner._semanticsOwner == null) {
_cachedSemanticsConfiguration = null;
return;
}
final bool wasSemanticsBoundary = _semantics != null && _cachedSemanticsConfiguration?.isSemanticBoundary == true;
_cachedSemanticsConfiguration = null;
bool isEffectiveSemanticsBoundary = _semanticsConfiguration.isSemanticBoundary && wasSemanticsBoundary;
RenderObject node = this;
while (!isEffectiveSemanticsBoundary && node.parent is RenderObject) {
if (node != this && node._needsSemanticsUpdate)
break;
node._needsSemanticsUpdate = true;
node = node.parent;
isEffectiveSemanticsBoundary = node._semanticsConfiguration.isSemanticBoundary;
if (isEffectiveSemanticsBoundary && node._semantics == null) {
return;
}
}
if (node != this && _semantics != null && _needsSemanticsUpdate) {
owner._nodesNeedingSemantics.remove(this);
}
if (!node._needsSemanticsUpdate) {
node._needsSemanticsUpdate = true;
if (owner != null) {
//记录需要更新语义的渲染对象
owner._nodesNeedingSemantics.add(node);
owner.requestVisualUpdate();
}
}
}
4.7.3 markNeedsPaint
[-> lib/src/rendering/object.dart]
void markNeedsPaint() {
if (_needsPaint)
return;
_needsPaint = true;
if (isRepaintBoundary) {
if (owner != null) {
//记录需要重新绘制的渲染对象
owner._nodesNeedingPaint.add(this);
owner.requestVisualUpdate();
}
} else if (parent is RenderObject) {
final RenderObject parent = this.parent;
parent.markNeedsPaint();
} else {
if (owner != null)
owner.requestVisualUpdate();
}
}
4.8 PipelineOwner.flushCompositingBits
[-> lib/src/rendering/object.dart]
void flushCompositingBits() {
profile(() { Timeline.startSync('Compositing bits'); });
_nodesNeedingCompositingBitsUpdate.sort((RenderObject a, RenderObject b) => a.depth - b.depth);
for (RenderObject node in _nodesNeedingCompositingBitsUpdate) {
//根据需要来决定是否更新位合成
if (node._needsCompositingBitsUpdate && node.owner == this)
node._updateCompositingBits(); // [见小节4.8.1]
}
_nodesNeedingCompositingBitsUpdate.clear(); //清空需要位合成的渲染对象
profile(() { Timeline.finishSync(); });
}
4.8.1 _updateCompositingBits
[-> lib/src/rendering/object.dart]
void _updateCompositingBits() {
if (!_needsCompositingBitsUpdate)
return;
final bool oldNeedsCompositing = _needsCompositing;
_needsCompositing = false;
visitChildren((RenderObject child) {
//遍历所有子项来更新位合成
child._updateCompositingBits();
if (child.needsCompositing)
_needsCompositing = true;
});
if (isRepaintBoundary || alwaysNeedsCompositing)
_needsCompositing = true;
if (oldNeedsCompositing != _needsCompositing)
markNeedsPaint();
_needsCompositingBitsUpdate = false;
}
4.9 PipelineOwner.flushPaint
[-> lib/src/rendering/object.dart]
void flushPaint() {
profile(() { Timeline.startSync('Paint', arguments: timelineWhitelistArguments); });
try {
final List<RenderObject> dirtyNodes = _nodesNeedingPaint;
_nodesNeedingPaint = <RenderObject>[];
//排序脏节点,深度最大的节点排第一位
for (RenderObject node in dirtyNodes..sort((RenderObject a, RenderObject b) => b.depth - a.depth)) {
if (node._needsPaint && node.owner == this) {
//此节点是否连接到树中,如果连接则重绘,否则跳过
if (node._layer.attached) {
PaintingContext.repaintCompositedChild(node); //[小节4.9.1]
} else {
node._skippedPaintingOnLayer();
}
}
}
} finally {
profile(() { Timeline.finishSync(); });
}
}
4.9.1 repaintCompositedChild
[-> lib/src/rendering/object.dart]
static void repaintCompositedChild(RenderObject child, { bool debugAlsoPaintedParent = false }) {
_repaintCompositedChild(
child,
debugAlsoPaintedParent: debugAlsoPaintedParent,
);
}
static void _repaintCompositedChild(
RenderObject child, {
bool debugAlsoPaintedParent = false,
PaintingContext childContext,
}) {
if (child._layer == null) {
child._layer = OffsetLayer();
} else {
child._layer.removeAllChildren();
}
childContext ??= PaintingContext(child._layer, child.paintBounds);
child._paintWithContext(childContext, Offset.zero);
childContext.stopRecordingIfNeeded();
}
4.10 RenderView.compositeFrame
[-> lib/src/rendering/view.dart]
void compositeFrame() {
Timeline.startSync('Compositing', arguments: timelineWhitelistArguments);
try {
//创建SceneBuilder [见小节4.10.1]
final ui.SceneBuilder builder = ui.SceneBuilder();
//创建Scene [见小节4.10.2]
final ui.Scene scene = layer.buildScene(builder);
if (automaticSystemUiAdjustment)
_updateSystemChrome();
ui.window.render(scene); // [见小节4.10.3]
scene.dispose();
} finally {
Timeline.finishSync();
}
}
该方法主要工作:
- 分别创建Flutter框架(dart)和引擎层(C++)的两个SceneBuilder;
- 分别创建Flutter框架(dart)和引擎层(C++)的两个Scene;
- 执行render()将layer树发送给GPU线程;
4.10.1 SceneBuilder初始化
[-> lib/ui/compositing.dart]
class SceneBuilder extends NativeFieldWrapperClass2 {
@pragma('vm:entry-point')
SceneBuilder() { _constructor(); }
void _constructor() native 'SceneBuilder_constructor';
...
}
SceneBuilder_constructor这是native方法,最终调用到引擎中的lib/ui/compositing/scene_builder.h中的SceneBuilder::create()方法, 创建C++的SceneBuilder对象。
4.10.2 OffsetLayer.buildScene
[-> lib/src/rendering/layer.dart]
ui.Scene buildScene(ui.SceneBuilder builder) {
updateSubtreeNeedsAddToScene(); //遍历layer树,将需要子树加入到scene
addToScene(builder); //将layer添加到SceneBuilder
return builder.build(); //调用C++层的build来构建Scene对象。
}
遍历layer树,将需要更新的全部都加入到SceneBuilder。再调用build(),同样也是native方法,执行SceneBuilder::build()来构建Scene对象。
4.10.3 Window::Render
[-> flutter/lib/ui/window/window.cc]
void Render(Dart_NativeArguments args) {
Dart_Handle exception = nullptr;
Scene* scene = tonic::DartConverter<Scene*>::FromArguments(args, 1, exception);
if (exception) {
Dart_ThrowException(exception);
return;
}
UIDartState::Current()->window()->client()->Render(scene); // [4.10.4]
}
ui.window.render()位于window.dart文件,这是一个native方法,会调用到window.cc的Render()方法。
4.10.4 RuntimeController::Render
[-> flutter/runtime/runtime_controller.cc]
void RuntimeController::Render(Scene* scene) {
//从scene中取出layer树 [见小节4.10.5]
client_.Render(scene->takeLayerTree());
}
4.10.5 Engine::Render
[-> flutter/shell/common/engine.cc]
void Engine::Render(std::unique_ptr<flow::LayerTree> layer_tree) {
if (!layer_tree)
return;
SkISize frame_size = SkISize::Make(viewport_metrics_.physical_width,
viewport_metrics_.physical_height);
if (frame_size.isEmpty())
return;
layer_tree->set_frame_size(frame_size);
animator_->Render(std::move(layer_tree)); // [4.10.6]
}
4.10.6 Animator::Render
[-> flutter/shell/common/animator.cc]
void Animator::Render(std::unique_ptr<flow::LayerTree> layer_tree) {
if (dimension_change_pending_ &&
layer_tree->frame_size() != last_layer_tree_size_) {
dimension_change_pending_ = false;
}
last_layer_tree_size_ = layer_tree->frame_size();
if (layer_tree) {
layer_tree->set_construction_time(fml::TimePoint::Now() -
last_begin_frame_time_);
}
//提交待处理的continuation,本次PipelineProduce完成 //[见小节4.10.7]
producer_continuation_.Complete(std::move(layer_tree));
delegate_.OnAnimatorDraw(layer_tree_pipeline_); //[见小节4.10.8]
}
UI线程的耗时从doFrame(frameTimeNanos)中的frameTimeNanos为起点,以Animator::Render()方法结束为终点, 并将结果保存到LayerTree的成员变量construction_time_,这便是UI线程的耗时时长。
4.10.7 ProducerContinuation.Complete
[-> flutter/synchronization/pipeline.h]
class ProducerContinuation {
void Complete(ResourcePtr resource) {
if (continuation_) {
continuation_(std::move(resource), trace_id_);
continuation_ = nullptr;
TRACE_EVENT_ASYNC_END0("flutter", "PipelineProduce", trace_id_);
TRACE_FLOW_STEP("flutter", "PipelineItem", trace_id_);
}
}
4.10.8 Shell::OnAnimatorDraw
[-> flutter/shell/common/shell.cc]
void Shell::OnAnimatorDraw(
fml::RefPtr<flutter::Pipeline<flow::LayerTree>> pipeline) {
//向GPU线程提交绘制任务
task_runners_.GetGPUTaskRunner()->PostTask(
[rasterizer = rasterizer_->GetWeakPtr(),
pipeline = std::move(pipeline)]() {
if (rasterizer) {
//由GPU线程来负责栅格化操作
rasterizer->Draw(pipeline);
}
});
}
这个方法主要是向GPU线程提交绘制任务。
4.11 PipelineOwner.flushSemantics
[-> lib/src/rendering/view.dart]
void flushSemantics() {
if (_semanticsOwner == null)
return;
profile(() { Timeline.startSync('Semantics'); });
try {
final List<RenderObject> nodesToProcess = _nodesNeedingSemantics.toList()
..sort((RenderObject a, RenderObject b) => a.depth - b.depth);
_nodesNeedingSemantics.clear();
//遍历_nodesNeedingSemantics,更新需要更新语义的渲染对象
for (RenderObject node in nodesToProcess) {
if (node._needsSemanticsUpdate && node.owner == this)
node._updateSemantics(); // [见小节4.11.1]
}
_semanticsOwner.sendSemanticsUpdate(); // 发送语义更新[见小节4.11.2]
} finally {
profile(() { Timeline.finishSync(); });
}
}
4.11.1 _updateSemantics
[-> lib/src/rendering/object.dart]
void _updateSemantics() {
if (_needsLayout) {
//此子树中没有足够的信息来计算语义,子树可能被视图窗口保持活着但没有布局
return;
}
final _SemanticsFragment fragment = _getSemanticsForParent(
mergeIntoParent: _semantics?.parent?.isPartOfNodeMerging ?? false,
);
final _InterestingSemanticsFragment interestingFragment = fragment;
final SemanticsNode node = interestingFragment.compileChildren(
parentSemanticsClipRect: _semantics?.parentSemanticsClipRect,
parentPaintClipRect: _semantics?.parentPaintClipRect,
).single;
}
4.11.2 sendSemanticsUpdate
[-> lib/src/semantics/semantics.dart]
void sendSemanticsUpdate() {
if (_dirtyNodes.isEmpty)
return;
final Set<int> customSemanticsActionIds = Set<int>();
final List<SemanticsNode> visitedNodes = <SemanticsNode>[];
while (_dirtyNodes.isNotEmpty) {
final List<SemanticsNode> localDirtyNodes = _dirtyNodes.where((SemanticsNode node) => !_detachedNodes.contains(node)).toList();
_dirtyNodes.clear();
_detachedNodes.clear();
localDirtyNodes.sort((SemanticsNode a, SemanticsNode b) => a.depth - b.depth);
visitedNodes.addAll(localDirtyNodes);
for (SemanticsNode node in localDirtyNodes) {
if (node.isPartOfNodeMerging) {
//如果合并到父节点,确保父节点已被添加到脏列表
if (node.parent != null && node.parent.isPartOfNodeMerging)
node.parent._markDirty(); //将节点添加到脏列表
}
}
}
visitedNodes.sort((SemanticsNode a, SemanticsNode b) => a.depth - b.depth);
final ui.SemanticsUpdateBuilder builder = ui.SemanticsUpdateBuilder();
for (SemanticsNode node in visitedNodes) {
if (node._dirty && node.attached)
node._addToUpdate(builder, customSemanticsActionIds);
}
_dirtyNodes.clear();
for (int actionId in customSemanticsActionIds) {
final CustomSemanticsAction action = CustomSemanticsAction.getAction(actionId);
builder.updateCustomAction(id: actionId, label: action.label, hint: action.hint, overrideId: action.action?.index ?? -1);
}
ui.window.updateSemantics(builder.build()); // [见小节4.11.3]
notifyListeners(); //通知已注册的监听器
}
可以看看监听器的数据,是否影响性能。
updateSemantics这是window.dart中的一个native方法,调用到如下方法。
4.11.3 Window::updateSemantics
[-> flutter/lib/ui/window/window.cc]
void UpdateSemantics(Dart_NativeArguments args) {
Dart_Handle exception = nullptr;
SemanticsUpdate* update =
tonic::DartConverter<SemanticsUpdate*>::FromArguments(args, 1, exception);
if (exception) {
Dart_ThrowException(exception);
return;
}
UIDartState::Current()->window()->client()->UpdateSemantics(update); // [见小节4.11.4]
}
4.11.4 RuntimeController::UpdateSemantics
[-> flutter/runtime/runtime_controller.cc]
void RuntimeController::UpdateSemantics(SemanticsUpdate* update) {
if (window_data_.semantics_enabled) {
client_.UpdateSemantics(update->takeNodes(), update->takeActions()); // [见小节4.11.5]
}
}
4.11.5 Engine::UpdateSemantics
[-> flutter/shell/common/engine.cc]
void Engine::UpdateSemantics(blink::SemanticsNodeUpdates update,
blink::CustomAccessibilityActionUpdates actions) {
delegate_.OnEngineUpdateSemantics(std::move(update), std::move(actions)); // [见小节4.11.6]
}
4.11.6 Shell::OnAnimatorDraw
[-> flutter/shell/common/shell.cc]
void Shell::OnEngineUpdateSemantics(
blink::SemanticsNodeUpdates update,
blink::CustomAccessibilityActionUpdates actions) {
task_runners_.GetPlatformTaskRunner()->PostTask(
[view = platform_view_->GetWeakPtr(), update = std::move(update),
actions = std::move(actions)] {
if (view) {
view->UpdateSemantics(std::move(update), std::move(actions));
}
});
}
这个方法主要是向平台线程提交Semantic任务。
再回到小节4.6,可知接下来再执行finalizeTree()操作;
4.12 BuildOwner.finalizeTree
[-> lib/src/widgets/framework.dart]
void finalizeTree() {
Timeline.startSync('Finalize tree', arguments: timelineWhitelistArguments);
try {
lockState(() {
//遍历所有的Element,执行unmount()动作,且取消GlobalKeys的注册
_inactiveElements._unmountAll();
});
} catch (e, stack) {
_debugReportException('while finalizing the widget tree', e, stack);
} finally {
Timeline.finishSync();
}
}
遍历所有的Element,执行相应具体Element子类的unmount()操作,下面以常见的StatefulElement为例来说明。
4.12.1 StatefulElement.unmount
[-> lib/src/widgets/framework.dart]
void unmount() {
super.unmount(); //[见小节4.12.2]
_state.dispose(); //执行State的dispose()方法
_state._element = null;
_state = null;
}
4.12.2 Element.unmount
[-> lib/src/widgets/framework.dart]
void unmount() {
if (widget.key is GlobalKey) {
final GlobalKey key = widget.key;
key._unregister(this); //取消GlobalKey的注册
}
}
附录
本文涉及到相关源码文件
flutter/shell/common/
- vsync_waiter.cc
- engine.cc
- animator.cc
- shell.cc
- rasterizer.cc
flutter/shell/platform/android/
- vsync_waiter_android.cc
- platform_view_android_jni.cc
- library_loader.cc
- io/flutter/view/VsyncWaiter.java
flutter/runtime/runtime_controller.cc
flutter/synchronization/pipeline.h
flutter/fml/message_loop_impl.cc
flutter/lib/ui/window/window.cc
flutter/lib/ui/window.dart
flutter/lib/ui/hooks.dart
lib/src/widgets/framework.dart
lib/src/widgets/binding.dart
lib/src/scheduler/binding.dart
lib/src/semantics/semantics.dart
lib/src/rendering/
- binding.dart
- object.dart
- view.dart
微信公众号 Gityuan | 微博 weibo.com/gityuan | 博客 留言区交流