基于Android 6.0的源码剖析, 加深对Refbase,sp/wp的认知.
system/core/libutils/RefBase.cpp
system/core/include/utils/RefBase.h
system/core/include/utils/StrongPointer.h
一. 概述
看过Android源码中的C++代码,一定不会对sp/wp感到陌生,系统中有大量存在sp/wp。RefBase是Android的native层(C++),有点类似Java世界的Object的味道。在Android Native体系架构中,通过RefBase,sp(strong pointer),wp(weak pointer) 这一系列强弱引用计数实现对对象生命周期的管理。
sp强指针其实就是一个模块类,先来看看其定义:
1.1 sp模块类
template<typename T>
class sp {
public:
inline sp() : m_ptr(0) { }
sp(T* other);
sp(const sp<T>& other); //对应于方法1
template<typename U> sp(U* other);
template<typename U> sp(const sp<U>& other);
~sp();
sp& operator = (T* other); //对应于方法2
sp& operator = (const sp<T>& other);
template<typename U> sp& operator = (const sp<U>& other);
template<typename U> sp& operator = (U* other);
void force_set(T* other);
void clear(); //重置
//重载Accessors
inline T& operator* () const { return *m_ptr; }
inline T* operator-> () const { return m_ptr; }
inline T* get() const { return m_ptr; }
//操作符
COMPARE(==)
COMPARE(!=)
COMPARE(>)
COMPARE(<)
COMPARE(<=)
COMPARE(>=)
private:
template<typename Y> friend class sp;
template<typename Y> friend class wp;
void set_pointer(T* ptr);
T* m_ptr; //指针
};
1.2 关系图
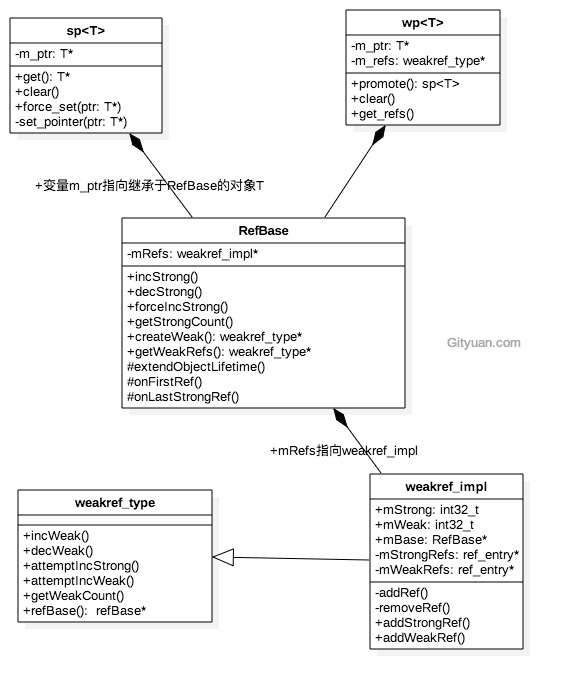
二. 源码分析
2.1 sp赋值过程
[-> StrongPointer.h]
位于StrongPointer.h文件,有4种方式来初始化sp对象,如下:
sp(T* other); //方式1
sp(const sp<T>& other); //方式2
sp& operator = (T* other); //方式3
sp& operator = (const sp<T>& other);//方式4
从以下实现来看,可知:
- 方式1和2,采用括号括号方式,则调用目标对象的incStrong()方法;
- 方式3和4,采用等号等号方式,则调用目标对象的incStrong()方法,再调用旧对象decStrong()方法;
括号方式1
template<typename T>
sp<T>::sp(T* other)
: m_ptr(other) {
if (other)
other->incStrong(this);
}
括号方式2
template<typename T>
sp<T>::sp(const sp<T>& other)
: m_ptr(other.m_ptr) {
if (m_ptr)
m_ptr->incStrong(this);
}
等号方式3
template<typename T>
sp<T>& sp<T>::operator =(const sp<T>& other) {
T* otherPtr(other.m_ptr);
if (otherPtr)
otherPtr->incStrong(this);
if (m_ptr)
m_ptr->decStrong(this);
m_ptr = otherPtr;
return *this;
}
等号方式4
template<typename T>
sp<T>& sp<T>::operator =(T* other) {
if (other)
other->incStrong(this);
if (m_ptr)
m_ptr->decStrong(this);
m_ptr = other;
return *this;
}
2.2 sp分析
Android源码中有大量的binder通信, ProcessState便是最常见的sp对象, 这里以该sp实例初始化为例,有如下两个方法:
sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self()); //采用括号方式2
sp<ProcessState> gProcess = new ProcessState; //采用等号方式4
说明:
- 其中ProcessState::self()返回的是sp
对象,可见proc(ProcessState::self())采用的是上面的模板中的括号方式2; - new ProcessState返回的是ProcessState指针,可见第2行采用的是等号方式4;
ProcessState继承于RefBase,所以初始化过程会初始化其父类RefBase。
2.3 RefBase构造函数
[-> RefBase.cpp]
RefBase::RefBase()
: mRefs(new weakref_impl(this))
{
}
RefBase初始化过程,会创建weakref_impl对象,继续已上述举例来说明,此处this为指向ProcessState的指针。 由此,可见创建ProcessState对象的同时,还会创建weakref_impl对象。
2.3.1 weakref_impl
[-> RefBase.cpp ::weakref_impl]
weakref_impl(RefBase* base)
: mStrong(INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) //强引用计数为 0x1000 0000
, mWeak(0) //弱引用计数为0
, mBase(base) //此时为ProcessState指针
, mFlags(0)
, mStrongRefs(NULL)
, mWeakRefs(NULL)
, mTrackEnabled(!!DEBUG_REFS_ENABLED_BY_DEFAULT)
, mRetain(false)
{
}
weakref_impl的成员变量mBase为ProcessState指针。 不管【小节2.2】哪种方式,最终都会调用目标对象的incStrong()方法,接下来说说该方法。
2.4 incStrong
[-> RefBase.cpp]
void RefBase::incStrong(const void* id) const
{
weakref_impl* const refs = mRefs;
refs->incWeak(id); //【见小节2.4.1】
refs->addStrongRef(id);
//增加强引用计数
const int32_t c = android_atomic_inc(&refs->mStrong);
if (c != INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
return;
}
//引用计数设置成1
android_atomic_add(-INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE, &refs->mStrong);
//当首次调用incStrong,则再回调onFirstRef;
refs->mBase->onFirstRef();
}
该方法的主要功能:
- 分别增加weakref_impl的强弱引用计数(mStrong/mWeak),进行加1操作;
- 当首次调用incStrong,则再回调目标对象的onFirstRef()方法,比如ProcessState对象。
2.4.1 incWeak
[-> RefBase.cpp ::weakref_type]
void RefBase::weakref_type::incWeak(const void* id)
{
weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this);
impl->addWeakRef(id);
//增加弱引用计数
const int32_t c __unused = android_atomic_inc(&impl->mWeak);
}
addWeakRef调用addRef(),非debug版本,该方法mTrackEnabled=false,则不做任何操作。 也就是代表着incWeak的工作就是mWeak引用计数+1。同理addStrongRef()方法也不做任何操作。
说完引用计数增加的方法,再来看看减少的方法decStrong。
2.5 RefBase析构函数
先来看看sp析构函数
2.5.1 sp析构函数
template<typename T>
sp<T>::sp(const sp<T>& other)
: m_ptr(other.m_ptr) {
if (m_ptr)
m_ptr->decStrong(this); //【见小节2.6】
}
2.5.2 RefBase析构函数
RefBase::~RefBase()
{
if (mRefs->mStrong == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
//释放weakref_impl对象
delete mRefs;
} else {
if ((mRefs->mFlags & OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) != OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) {
//非STRONG模式下,弱引用计数为0,则释放weakref_impl对象
if (mRefs->mWeak == 0) {
delete mRefs;
}
}
}
const_cast<weakref_impl*&>(mRefs) = NULL;
}
2.6 decStrong
[-> RefBase.cpp]
void RefBase::decStrong(const void* id) const
{
weakref_impl* const refs = mRefs;
refs->removeStrongRef(id);
//强引用减一,返回值是执行减一操作前的mStrong旧值。
const int32_t c = android_atomic_dec(&refs->mStrong);
if (c == 1) {
refs->mBase->onLastStrongRef(id);
if ((refs->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) {
delete this; //当lifetime为OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG,则回收该对象
}
}
//【见小节2.6.1】
refs->decWeak(id);
}
该方法的主要功能:
- 分别减少weakref_impl的强弱引用计数(mStrong/mWeak),进行减1操作;
- 当调用decStrong调用结束后引用计数为0,则再回调目标对象的onLastStrongRef()方法;
- 同时OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG模式时,还会释放目标对象。
2.6.1 decWeak
[-> RefBase.cpp ::weakref_type]
void RefBase::weakref_type::decWeak(const void* id)
{
weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this);
impl->removeWeakRef(id);
//mWeak执行减一操作
const int32_t c = android_atomic_dec(&impl->mWeak);
if (c != 1) return;
//弱引用计数减到零的情况。
if ((impl->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) {
if (impl->mStrong == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
//释放实际目标对象
delete impl->mBase;
} else {
//释放weakref_impl对象
delete impl;
}
} else {
//低频场景:lifetime为OBJECT_LIFETIME_{WEAK|FOREVER}
impl->mBase->onLastWeakRef(id);
if ((impl->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK) {
//作为OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK,则删除实际对象。
delete impl->mBase;
}
}
}
当强弱引用都减到0,普遍常见是会把实际对象和weakref_impl对象都释放。
三. 总结
- sp/wp是模块类, 超载操作符,比如=,->, *
- RefBase是Android C++类的父类
- weakref_impl是weakref_type的子类
3.1 RefBase
RefBase有一个成员变量mRefs为weakref_impl指针,weakref_impl对象便是用来管理引用计数的。
| 引用类型 | 强引用计数 | 弱引用计数 |
|---|---|---|
| sp构造 | +1 | +1 |
| wp构造 | +1 | |
| sp析构 | -1 | -1 |
| wp析构 | -1 |
对于绝大多数的最常见的是OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG:
- sp初始化过程,在构造一个实际对象的同时,会自动创建一个weakref_impl对象;并且强弱引用计数分别加1;
- 强引用为0时,实际对象被delete;
- 弱引用为0时,weakref_impl对象被delete;
注意:首次调用对象incStrong(),则会调用该对象的onFirstRef(). 调用decStrong()的最后一次,则会调用该对象的onLastStrongRef().
另外,对于弱引用不能直接操作目标对象,根本原因是在于弱指针类没有重载*和->操作符号,而强指针重载了这两个操作符号。可通过promote()函数,将弱引用提升为强引用对象
- promote作用试图增加目标对象的强引用计数;
- 由于目标对象可能已经被delete掉了,或者是其它的原因导致提升失败;
3.2 生命周期
- flags为OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG,强引用计数控制实际对象的生命周期,弱引用计数控制weakref_impl对象的生命周期。
- 强引用计数为0后,实际对象被delete。所以对于这种情况,应使用wp时要由弱生强。
- flags为LIFETIME_WEAK,强引用计数为0,弱引用计数不为0时,实际对象不会被delete。
- 当弱引用计数减为0时,实际对象和weakref_impl对象会同时被delete。
- flags为LIFETIME_FOREVER,对象不受强弱引用计数的控制,永不会被回收。
关于sp好处就是让系统根据引用计数来自动管理对象的回收问题,多增加了管理对象,故其执行效率会比普通指针略低。
微信公众号 Gityuan | 微博 weibo.com/gityuan | 博客 留言区交流