基于Android 6.0的源码剖析, 分析bind service的启动流程。
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/LoadedApk.java
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/IServiceConnection.aidl
一. 概述
文章startService启动过程分析,介绍了 startService的过程,本文介绍通过bind方式来启动服务。
1.1 实例
定义AIDL文件:
interface IRemoteService {
String getBlog();
}
服务端(远程服务进程)
public class RemoteService extends Service {
...
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBnRemoteService;
}
//IRemoteService.Stub 便是由AIDL文件IRemoteService自动生成的
private final IRemoteService.Stub mBnRemoteService = new IRemoteService.Stub() {
@Override
public String getBlog() throws RemoteException {
return ”www.gityuan.com;
}
};
}
Client端(发起端进程)
private IRemoteService mBpRemoteService;
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
mBpRemoteService = IRemoteService.Stub.asInterface(service);
//通过Binder最终会调用远程服务中同名方法来执行,这便完成了一次跨进程
mBpRemoteService.getBlog();
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
mRemoteService = null;
}
};
Intent intent = new Intent(this, RemoteService.class);
//Client端通过bindService去绑定远程服务【见下文】
bindService(intent, mConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
二. 发起端进程
1. CW.bindService
[-> ContextWrapper.java]
public class ContextWrapper extends Context {
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
//其中mBase为ContextImpl对象 【见流程2】
return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
}
}
2. CI.bindService
[-> ContextImpl.java]
class ContextImpl extends Context {
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
//【见流程3】
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, Process.myUserHandle());
}
}
3. CI.bindServiceCommon
[-> ContextImpl.java]
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
...
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
//获取的是内部静态类InnerConnection【见小节3.1】
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(),
mMainThread.getHandler(), flags);
} else {
...
}
try {
...
//[见流程4]
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
...
return res != 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
}
该方法主要功能:
- 创建对象内部静态类LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection的对象;
- 通过IActivityManager接口,向AMS发送bind请求.
这里需要注意的是mMainThread.getApplicationThread()方法返回的是ApplicationThread对象, 该对象继承于ApplicationThreadNative(Binder服务端)
3.1 getServiceDispatcher
[-> LoadedApk.java]
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> map = mServices.get(context);
if (map != null) {
sd = map.get(c);
}
if (sd == null) {
//创建服务分发对象【见小节3.2】
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>();
mServices.put(context, map);
}
//以ServiceConnection为key, ServiceDispatcher为value保存到map
map.put(c, sd);
} else {
sd.validate(context, handler);
}
//返回的内部类的对象InnerConnection【见小节3.2】
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
说明:
- mServices记录着所有context里面, 每个ServiceConnection以及所对应的LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher对象;同一个ServiceConnection只会创建一次;
- 返回的对象是LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection,该对象继承于IServiceConnection.Stub, 该类是由IServiceConnection.aidl自动生成的 作为binder服务端。
- 这里需要注意的是IServiceConnection是属于oneway interface,也就是非阻塞的binder call.
3.2 ServiceDispatcher
[-> LoadedApk.java ::ServiceDispatcher]
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
//内部类
private final ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection mIServiceConnection;
//用户传递的参数
private final ServiceConnection mConnection;
private final Context mContext;
private final Handler mActivityThread;
private final ServiceConnectionLeaked mLocation;
//用户传递的参数
private final int mFlags;
private boolean mDied;
private boolean mForgotten;
ServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection conn,
Context context, Handler activityThread, int flags) {
//创建InnerConnection对象
mIServiceConnection = new InnerConnection(this);
//用户定义的ServiceConnection
mConnection = conn;
mContext = context;
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mLocation = new ServiceConnectionLeaked(null);
mLocation.fillInStackTrace();
mFlags = flags;
}
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}
//获取内部类的InnerConnection对象
IServiceConnection getIServiceConnection() {
return mIServiceConnection;
}
}
ServiceDispatcher是LoadedApk的静态内部类。InnerConnection是ServiceDispatcher的静态内部类, 通过getIServiceConnection()方法返回的便是构造方法中创建的InnerConnection对象.
4. AMP.bindService
[-> ActivityManagerNative.java :: AMP]
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token,
Intent service, String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection,
int flags, String callingPackage, int userId) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
service.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
//将InnerConnection对象传递system_server
data.writeStrongBinder(connection.asBinder());
data.writeInt(flags);
data.writeString(callingPackage);
data.writeInt(userId);
//通过bind调用,进入system_server【见流程5】
mRemote.transact(BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int res = reply.readInt();
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
return res;
}
经过Binder IPC便进入了system_server进程.
三. system_server端
5. AMN.onTransact
public boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags)
throws RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION: {
data.enforceInterface(IActivityManager.descriptor);
IBinder b = data.readStrongBinder();
//此处b为ApplicationThread的, 转换后生成即ApplicationThreadProxy对象
IApplicationThread app = ApplicationThreadNative.asInterface(b);
IBinder token = data.readStrongBinder();
Intent service = Intent.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
String resolvedType = data.readString();
b = data.readStrongBinder();
int fl = data.readInt();
String callingPackage = data.readString();
int userId = data.readInt();
//生成InnerConnectiond的代理对象
IServiceConnection conn = IServiceConnection.Stub.asInterface(b);
//【见流程6】
int res = bindService(app, token, service, resolvedType, conn, fl,
callingPackage, userId);
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(res);
return true;
}
...
}
}
该方法的主要功能:
- 参数app: 根据发起端进程传递过来的ApplicationThread对象(Binder服务端), 通过asInterface()方法生成新的代理对象ApplicationThreadProxy类型对象app;
- 参数conn: 根据发起端进程传递过来的InnerConnectiond对象(Binder服务端),同样通过转换后,生成IServiceConnection.Stub.Proxy类型对象conn;
- 参数service: 数据类型为Intent, 是指本次要启动的service的意图;
- 参数callingPackage: 发起方所属的包名;
- 参数fl: 是指flags, 此时等于Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE, 即值为1.
将这些参数传递给AMS来处理
6. AMS.bindService
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String callingPackage,
int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
synchronized(this) {
//【见流程7】
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
7. AS.bindServiceLocked
[-> ActiveServices.java]
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String callingPackage, int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//查询发起端所对应的进程记录结构
final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
...
ActivityRecord activity = null;
//token不为空, 代表着发起方具有activity上下文
if (token != null) {
activity = ActivityRecord.isInStackLocked(token);
if (activity == null) {
return 0; //存在token, 却找不到activity为空,则直接返回
}
}
int clientLabel = 0;
PendingIntent clientIntent = null;
if (callerApp.info.uid == Process.SYSTEM_UID) {
... //发起方是system进程的情况
}
...
//根据发送端所在进程的SchedGroup来决定是否为前台service.
final boolean callerFg = callerApp.setSchedGroup != Process.THREAD_GROUP_BG_NONINTERACTIVE;
//根据用户传递进来Intent来检索相对应的服务【见流程7.1】
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, callingPackage,
Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), userId, true, callerFg);
if (res == null) {
return 0;
}
if (res.record == null) {
return -1;
}
//查询到相应的Service
ServiceRecord s = res.record;
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
//取消服务的重启调度
unscheduleServiceRestartLocked(s, callerApp.info.uid, false);
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
//更新当前service活动时间
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
...
}
mAm.startAssociationLocked(callerApp.uid, callerApp.processName,
s.appInfo.uid, s.name, s.processName);
//【见流程7.2】
AppBindRecord b = s.retrieveAppBindingLocked(service, callerApp);
//创建对象ConnectionRecord,此处connection来自发起方
ConnectionRecord c = new ConnectionRecord(b, activity,
connection, flags, clientLabel, clientIntent);
IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = s.connections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
clist = new ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>();
s.connections.put(binder, clist);
}
clist.add(c); // clist是ServiceRecord.connections的成员变量
b.connections.add(c); //b是指AppBindRecord
if (activity != null) {
if (activity.connections == null) {
activity.connections = new HashSet<ConnectionRecord>();
}
activity.connections.add(c);
}
b.client.connections.add(c);
if ((c.flags&Context.BIND_ABOVE_CLIENT) != 0) {
b.client.hasAboveClient = true;
}
if (s.app != null) {
updateServiceClientActivitiesLocked(s.app, c, true);
}
clist = mServiceConnections.get(binder);
if (clist == null) {
clist = new ArrayList<ConnectionRecord>();
mServiceConnections.put(binder, clist);
}
clist.add(c);
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
//启动service,这个过程跟startService过程一致【见小节8】
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false) != null) {
return 0;
}
}
if (s.app != null) {
if ((flags&Context.BIND_TREAT_LIKE_ACTIVITY) != 0) {
s.app.treatLikeActivity = true;
}
//更新service所在进程的优先级
mAm.updateLruProcessLocked(s.app, s.app.hasClientActivities
|| s.app.treatLikeActivity, b.client);
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked(s.app);
}
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
try {
//Service已经正在运行,则调用InnerConnection的代理对象
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder);
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
//当第一个app连接到该binding, 且之前已被bind过, 则回调onRebind()方法
if (b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true);
}
} else if (!b.intent.requested) {
//最终回调onBind()方法
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, false);
}
getServiceMap(s.userId).ensureNotStartingBackground(s);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return 1;
}
该方法主要功能:
- 通过retrieveServiceLocked(),根据用户传递进来Intent来检索相对应的服务
- 通过retrieveAppBindingLocked().创建AppBindRecord对象记录着当前ServiceRecord, intent以及发起方的进程信息。
- 通过bringUpServiceLocked()拉起目标服务;
另外, 将发起发传递过来的LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection的代理对象, 即IServiceConnection.Stub.Proxy类型对象connection, 保存到新创建的ConnectionRecord对象的成员变量. 再通过clist.add(c), 将该ConnectionRecord对象添加到clist队列. 后面便可以通过clist来 查询发起方的信息.
7.1 AS.retrieveServiceLocked
[-> ActiveServices.java]
private ServiceLookupResult retrieveServiceLocked(Intent service,
String resolvedType, String callingPackage, int callingPid, int callingUid, int userId,
boolean createIfNeeded, boolean callingFromFg) {
ServiceRecord r = null;
userId = mAm.handleIncomingUser(callingPid, callingUid, userId,
false, ActivityManagerService.ALLOW_NON_FULL_IN_PROFILE, "service", null);
ServiceMap smap = getServiceMap(userId);
final ComponentName comp = service.getComponent();
if (comp != null) {
//根据服务名查找相应的ServiceRecord
r = smap.mServicesByName.get(comp);
}
if (r == null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter = new Intent.FilterComparison(service);
//根据Intent查找相应的ServiceRecord
r = smap.mServicesByIntent.get(filter);
}
if (r == null) {
try {
//通过PKMS来查询相应的service
ResolveInfo rInfo =
AppGlobals.getPackageManager().resolveService(
service, resolvedType,
ActivityManagerService.STOCK_PM_FLAGS, userId);
ServiceInfo sInfo = rInfo != null ? rInfo.serviceInfo : null;
if (sInfo == null) {
return null;
}
//获取组件名
ComponentName name = new ComponentName(
sInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, sInfo.name);
if (userId > 0) {
//服务是否属于单例模式
if (mAm.isSingleton(sInfo.processName, sInfo.applicationInfo,
sInfo.name, sInfo.flags)
&& mAm.isValidSingletonCall(callingUid, sInfo.applicationInfo.uid)) {
userId = 0;
smap = getServiceMap(0);
}
sInfo = new ServiceInfo(sInfo);
sInfo.applicationInfo = mAm.getAppInfoForUser(sInfo.applicationInfo, userId);
}
r = smap.mServicesByName.get(name);
if (r == null && createIfNeeded) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(service.cloneFilter());
//创建Restarter对象
ServiceRestarter res = new ServiceRestarter();
...
//创建ServiceRecord对象
r = new ServiceRecord(mAm, ss, name, filter, sInfo, callingFromFg, res);
res.setService(r);
smap.mServicesByName.put(name, r);
smap.mServicesByIntent.put(filter, r);
//确保该组件不再位于pending队列
for (int i=mPendingServices.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ServiceRecord pr = mPendingServices.get(i);
if (pr.serviceInfo.applicationInfo.uid == sInfo.applicationInfo.uid
&& pr.name.equals(name)) {
mPendingServices.remove(i);
}
}
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
//运行在同一个进程,不会发生RemoteException
}
}
if (r != null) {
//各种权限检查,不满足条件则返回为null的service
if (mAm.checkComponentPermission(r.permission,
callingPid, callingUid, r.appInfo.uid, r.exported)
!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
//当exported=false则不允许启动
if (!r.exported) {
return new ServiceLookupResult(null, "not exported from uid "
+ r.appInfo.uid);
}
return new ServiceLookupResult(null, r.permission);
} else if (r.permission != null && callingPackage != null) {
final int opCode = AppOpsManager.permissionToOpCode(r.permission);
if (opCode != AppOpsManager.OP_NONE && mAm.mAppOpsService.noteOperation(
opCode, callingUid, callingPackage) != AppOpsManager.MODE_ALLOWED) {
return null;
}
}
if (!mAm.mIntentFirewall.checkService(r.name, service, callingUid, callingPid,
resolvedType, r.appInfo)) {
return null;
}
//创建Service查询结果对象
return new ServiceLookupResult(r, null);
}
return null;
}
服务查询过程:
- 根据服务名从ServiceMap.mServicesByName中查找相应的ServiceRecord,如果没有找到,则往下执行;
- 根据Intent从ServiceMap.mServicesByIntent中查找相应的ServiceRecord,如果还是没有找到,则往下执行;
- 通过PKMS来查询相应的ServiceInfo,如果仍然没有找到,则不再往下执行。
属于isSingleton的情况有以下3类:
- 组件uid>10000,且同时具有ServiceInfo.FLAG_SINGLE_USER flags和INTERACT_ACROSS_USERS权限;
- 组件运行在system进程的情况;
- 具有ServiceInfo.FLAG_SINGLE_USER flags,且uid=Process.PHONE_UID或者persistent app的情况;
7.2 SR.retrieveAppBindingLocked
[-> ServiceRecord.java]
public AppBindRecord retrieveAppBindingLocked(Intent intent,
ProcessRecord app) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter = new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord i = bindings.get(filter);
if (i == null) {
//创建连接ServiceRecord和filter的记录信息
i = new IntentBindRecord(this, filter);
bindings.put(filter, i);
}
//此处app是指调用方所在进程
AppBindRecord a = i.apps.get(app);
if (a != null) {
return a;
}
//创建ServiceRecord跟进程绑定的记录信息
a = new AppBindRecord(this, i, app);
i.apps.put(app, a);
return a;
}
AppBindRecord对象记录着当前ServiceRecord,intent以及发起方的进程信息。
8. bringUpServiceLocked
[-> ActiveServices.java]
private final String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
// 进程已存在的情况
if (r.app != null && r.app.thread != null) {
//调用service.onStartCommand()过程
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, false);
return null;
}
....
//服务正在启动,设置package停止状态为false
AppGlobals.getPackageManager().setPackageStoppedState(
r.packageName, false, r.userId);
ProcessRecord app;
if (!isolated) {
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.versionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
// 启动服务 【见流程9】
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
}
//对于进程没有启动的情况
if (app == null) {
//启动service所要运行的进程,最终还是会调用到【见流程9】
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
"service", r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
...
return msg;
}
}
if (!mPendingServices.contains(r)) {
mPendingServices.add(r);
}
...
return null;
}
9. realStartServiceLocked
[-> ActiveServices.java]
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
...
r.app = app;
r.restartTime = r.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
final boolean newService = app.services.add(r);
//发送delay消息
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "create");
boolean created = false;
try {
...
mAm.ensurePackageDexOpt(r.serviceInfo.packageName);
app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
//服务进入 onCreate() 【见流程10】
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
r.postNotification();
created = true;
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
mAm.appDiedLocked(app); //应用死亡处理
throw e;
} finally {
if (!created) {
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
if (newService) {
app.services.remove(r);
r.app = null;
}
//尝试重新启动服务
if (!inDestroying) {
scheduleServiceRestartLocked(r, false);
}
}
}
//【见流程12】
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
updateServiceClientActivitiesLocked(app, null, true);
if (r.startRequested && r.callStart && r.pendingStarts.size() == 0) {
r.pendingStarts.add(new ServiceRecord.StartItem(r, false, r.makeNextStartId(),
null, null));
}
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
if (r.delayed) {
getServiceMap(r.userId).mDelayedStartList.remove(r);
r.delayed = false;
}
...
}
该方法有几个重要的时间点:
- bumpServiceExecutingLocked;
- AT.scheduleCreateService;
- requestServiceBindingsLocked;
- AT.sendServiceArgsLocked;
三. 远程服务进程
10. scheduleCreateService
[-> ApplicationThread.java]
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData(); //准备服务创建所需的数据
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
//发送消息 【见流程11】
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}
通过handler机制, 将H.CREATE_SERVICE消息发送给远程服务进程的主线程的handler来处理
11. AT.handleCreateService
[-> ActivityThread.java]
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
//当应用处于后台即将进行GC,而此时被调回到活动状态,则跳过本次gc。
unscheduleGcIdler();
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
//通过反射创建目标服务对象
Service service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
...
try {
//创建ContextImpl对象
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
//创建Application对象
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
//调用服务onCreate()方法 [见小节11.1]
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
//调用服务创建完成
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
}
再回到前面的【流程9】realStartServiceLocked()过程,执行完scheduleCreateService()操作, 接下来,继续回到system_server进程,开始执行requestServiceBindingsLocked过程。
11.1 onCreate
[-> Service.java]
public void onCreate() {
}
用户自行覆写该方法, 也可以选择不覆写该方法.
四. system_server端
12. requestServiceBindingsLocked
[-> ActiveServices.java]
private final void requestServiceBindingsLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
for (int i=r.bindings.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
IntentBindRecord ibr = r.bindings.valueAt(i);
//[见流程13]
if (!requestServiceBindingLocked(r, ibr, execInFg, false)) {
break;
}
}
}
通过bindService方式启动的服务, 那么该serviceRecord的bindings则一定不会空.
13. requestServiceBindingLocked
[-> ActiveServices.java]
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null) {
return false;
}
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
try {
//发送bind开始的消息
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "bind");
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
//服务进入 onBind() 【见流程14】
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind, r.app.repProcState);
if (!rebind) {
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
14. ATP.scheduleBindService
[-> ApplicationThreadProxy.java]
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent, boolean rebind,
int processState) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeInt(rebind ? 1 : 0);
data.writeInt(processState);
//【见流程15】
mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, null,
IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
data.recycle();
}
五. 远程服务进程
15. ATN.onTransact
[-> ApplicationThreadNative.java]
public boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags)
throws RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case SCHEDULE_BIND_SERVICE_TRANSACTION: {
data.enforceInterface(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
IBinder token = data.readStrongBinder();
Intent intent = Intent.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
boolean rebind = data.readInt() != 0;
int processState = data.readInt();
//【见流程13】
scheduleBindService(token, intent, rebind, processState);
return true;
}
...
}
13. scheduleBindService
[-> ApplicationThread.java]
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent,
boolean rebind, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.intent = intent;
s.rebind = rebind;
//【见流程14】
sendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}
通过handler机制, 将H.BIND_SERVICE消息发送给远程服务进程的主线程的handler来处理
14. AT.handleBindService
[-> ActivityThread.java]
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
if (!data.rebind) {
// 执行Service.onBind()回调方法 [见小节14.1]
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
//将onBind返回值传递回去【见流程15】
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
ensureJitEnabled();
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
}
}
14.1 onRebind
[-> Service.java]
public abstract IBinder onBind(Intent intent);
Service的onBind()是抽象方法, 所以大家创建Service子类时必须要覆写该方法, 返回IBinder对象, 也可以直接返回NULL.
15. AMP.publishService
[-> ActivityManagerNative.java ::ActivityManagerProxy]
public void publishService(IBinder token,
Intent intent, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
//将service.onBind的返回值传递给远程进程
data.writeStrongBinder(service);
// [见流程16]
mRemote.transact(PUBLISH_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
}
经过Binder IPC进入system_server进程交由AMS来处理
六. system_server进程
16. AMS.publishService
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
...
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
//【见流程17】
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}
远程服务的onBind()的返回值的IBinder(Bn端), 在AMP.publishService()过程中经过data.writeStrongBinder(service)传递到底层, 再回到system_server进程中AMN.onTransact()中经过data.readStrongBinder()方法会获取该service所相对应的代理对象(Bp端).
简言之,此处的IBinder类型的service就是远程服务进程中的Bp端对象.
17. publishServiceLocked
[-> ActiveServices.java]
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter = new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i<clist.size(); i++) {
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
if (!filter.equals(c.binding.intent.intent)) {
continue;
}
try {
//【见流程18】
c.conn.connected(r.name, service);
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
}
}
}
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, mDestroyingServices.contains(r), false);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
[小节7]AS.bindServiceLocked的过程中初始化, 可知c.conn是指通往发起端进程的IServiceConnection.Stub.Proxy代理对象. 通过Binder IPC调用, 进入发起方进程的IServiceConnection.Stub对象. 由于LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection 继承于IServiceConnection.Stub. 所以,接下来便由回到发起方进程中的InnerConnection对象.
七. 发起方进程
18. InnerConnection.connected
[-> LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection]
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service); //[见流程19]
}
}
}
19. ServiceDispatcher.connected
[-> LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher]
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (mActivityThread != null) {
//这是主线程的Handler 【见流程20】
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0));
} else {
doConnected(name, service);
}
}
20. RunConnection.run
[-> LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.RunConnection]
private final class RunConnection implements Runnable {
RunConnection(ComponentName name, IBinder service, int command) {
mName = name;
mService = service;
mCommand = command; //此时为0
}
public void run() {
if (mCommand == 0) {
doConnected(mName, mService); //【见流程21】
} else if (mCommand == 1) {
doDeath(mName, mService);
}
}
final ComponentName mName;
final IBinder mService;
final int mCommand;
}
- 此处的mName是指远程服务的组件名对象ComponentName;
- 此处的mService是指远程服务的onBind()返回的IBinder代理对象;
21. doConnected
[-> LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher]
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo old;
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo info;
synchronized (this) {
if (mForgotten) {
return;
}
old = mActiveConnections.get(name);
if (old != null && old.binder == service) {
return;
}
if (service != null) {
mDied = false;
info = new ConnectionInfo();
info.binder = service;
//创建死亡监听对象
info.deathMonitor = new DeathMonitor(name, service);
try {
//建立死亡通知
service.linkToDeath(info.deathMonitor, 0);
mActiveConnections.put(name, info);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
return;
}
} else {
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
}
if (old != null) {
old.binder.unlinkToDeath(old.deathMonitor, 0);
}
}
if (old != null) {
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
if (service != null) {
//回调用户定义的ServiceConnection()
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
}
}
此处创建了死亡监听对象,也是内部类:LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.DeathMonitor,定义如下:
private final class DeathMonitor implements IBinder.DeathRecipient
{
DeathMonitor(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
mName = name;
mService = service;
}
public void binderDied() {
death(mName, mService); //【见流程18.2】
}
final ComponentName mName;
final IBinder mService;
}
八. 总结
整体调用流程图:大图
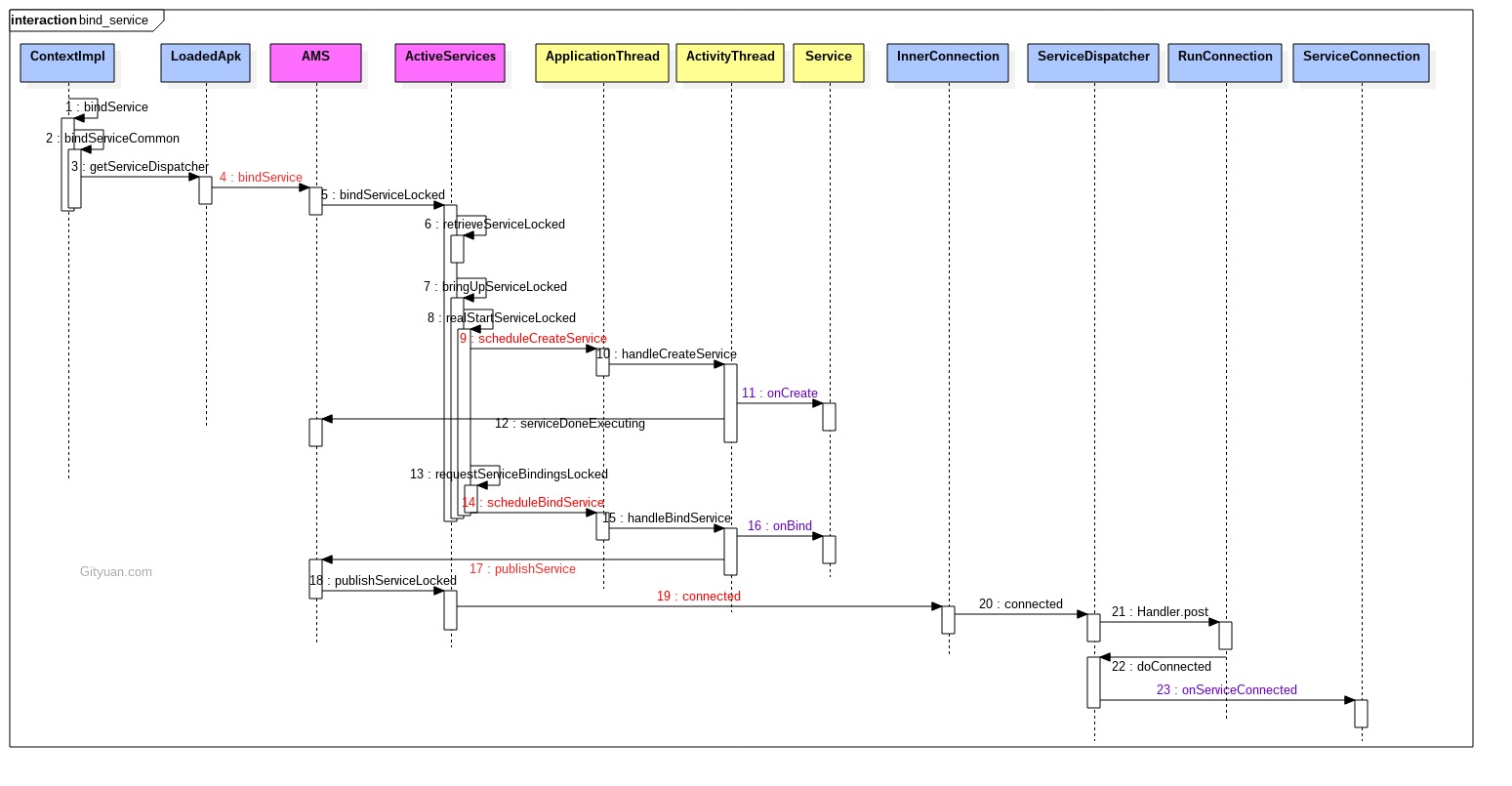
说明:
- 图中蓝色代表的是Client进程(发起端), 红色代表的是system_server进程, 黄色代表的是target进程(service所在进程);
- Client进程: 通过getServiceDispatcher获取Client进程的匿名Binder服务端,即LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection,该对象继承于IServiceConnection.Stub; 再通过bindService调用到system_server进程;
- system_server进程: 依次通过scheduleCreateService和scheduleBindService方法, 远程调用到target进程; 4: target进程: 依次执行onCreate()和onBind()方法; 将onBind()方法的返回值IBinder(作为target进程的binder服务端)通过publishService传递到system_server进程;
- system_server进程: 利用IServiceConnection代理对象向Client进程发起connected()调用, 并把target进程的onBind返回Binder对象的代理端传递到Client进程;
- Client进程: 回调到onServiceConnection()方法, 该方法的第二个参数便是target进程的binder代理端. 到此便成功地拿到了target进程的代理, 可以畅通无阻地进行交互.
微信公众号 Gityuan | 微博 weibo.com/gityuan | 博客 留言区交流